Understanding Warehouse Automation
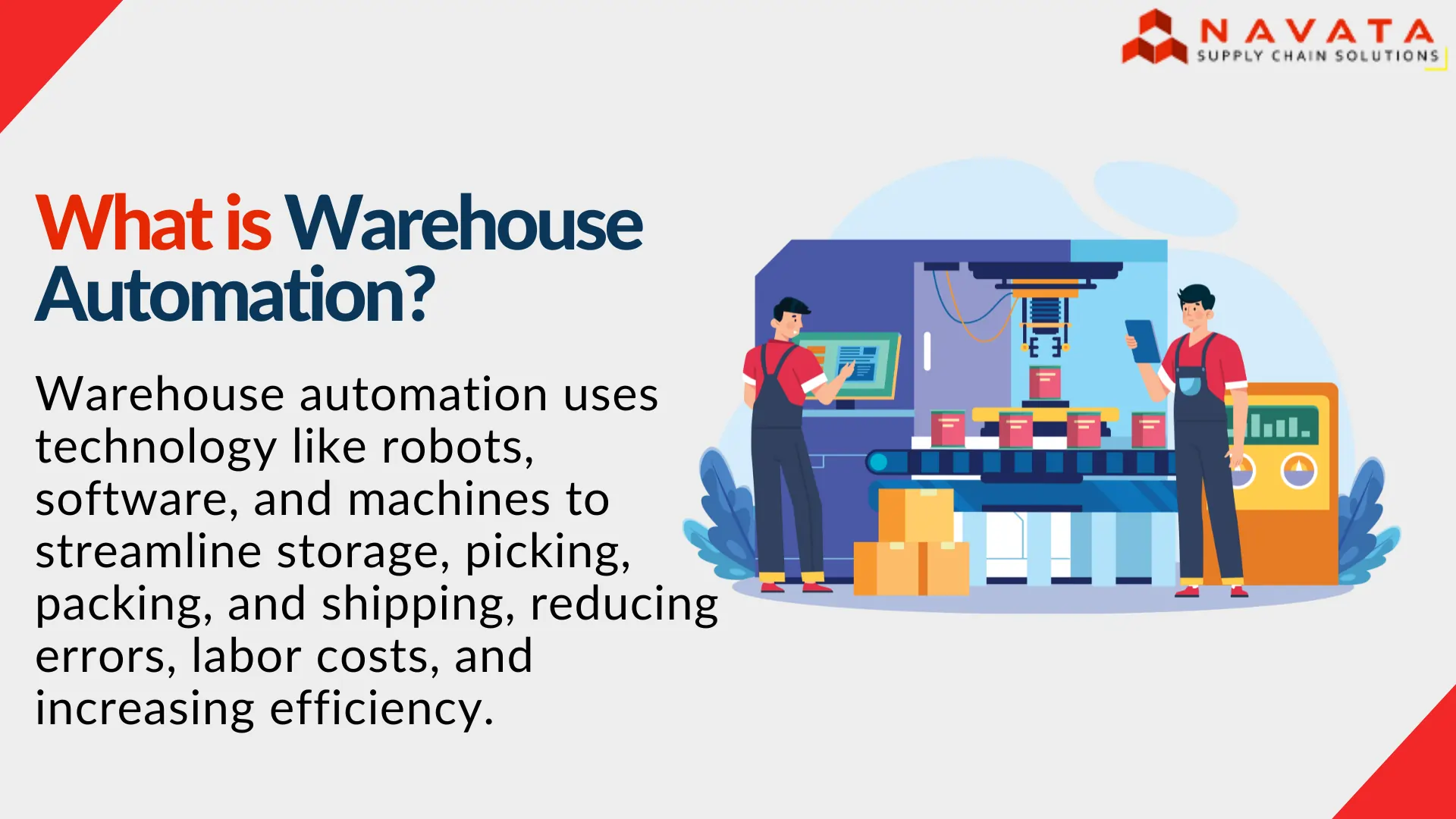
Warehouse automation is the process of using technology to streamline and enhance various warehouse operations, such as storing, picking, packing, and shipping goods. The automation process includes basic conveyor belts and barcode scanners alongside advanced robotics and automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and intelligent software systems. The primary objective is to reduce human employees while simultaneously reducing mistakes during order processing, shortening delivery times, and decreasing operational expenses.
The need for faster deliveries and real-time tracking by consumers drives business success through automation because it provides operational efficiency. The system enhances inventory precision while it makes workplaces safer and enables warehouses to grow without adding equivalent personnel or facilities. Warehouse automation stands as the core element for creating an agile and smarter supply chain system.
Why Do Warehouses Need Automation?
A massive warehouse contains thousands of products stored inside its space. Under current conditions, workers must traverse extensive distances while doing manual item searches before they carry products to packing areas and get them ready for shipment. The whole process turns out to be time-intensive while also being exhausting for workers and prone to human errors.
The same warehouse receives added value through conveyor belts moving goods automatically together with barcode scanners that instantly track inventory and robotic transport vehicles for optimized efficiency. Software systems direct employees to precise item locations, which decreases both labor time consumption and workplace confusion.
Warehouse automation systems generate multiple important advantages. The system enables faster operational speed, which enables workers to handle greater order volumes within shorter periods. The system minimizes human mistakes to increase order precision. The automation system reduces labour expenses because it eliminates repetitive tasks that require manual work.
The implementation of automated systems enhances safety measures through the removal of both unsafe lifting activities and dangerous work tasks. The combination of faster delivery with more reliable services leads to enhanced customer satisfaction, which grants businesses an advantage in the current fast-moving market.
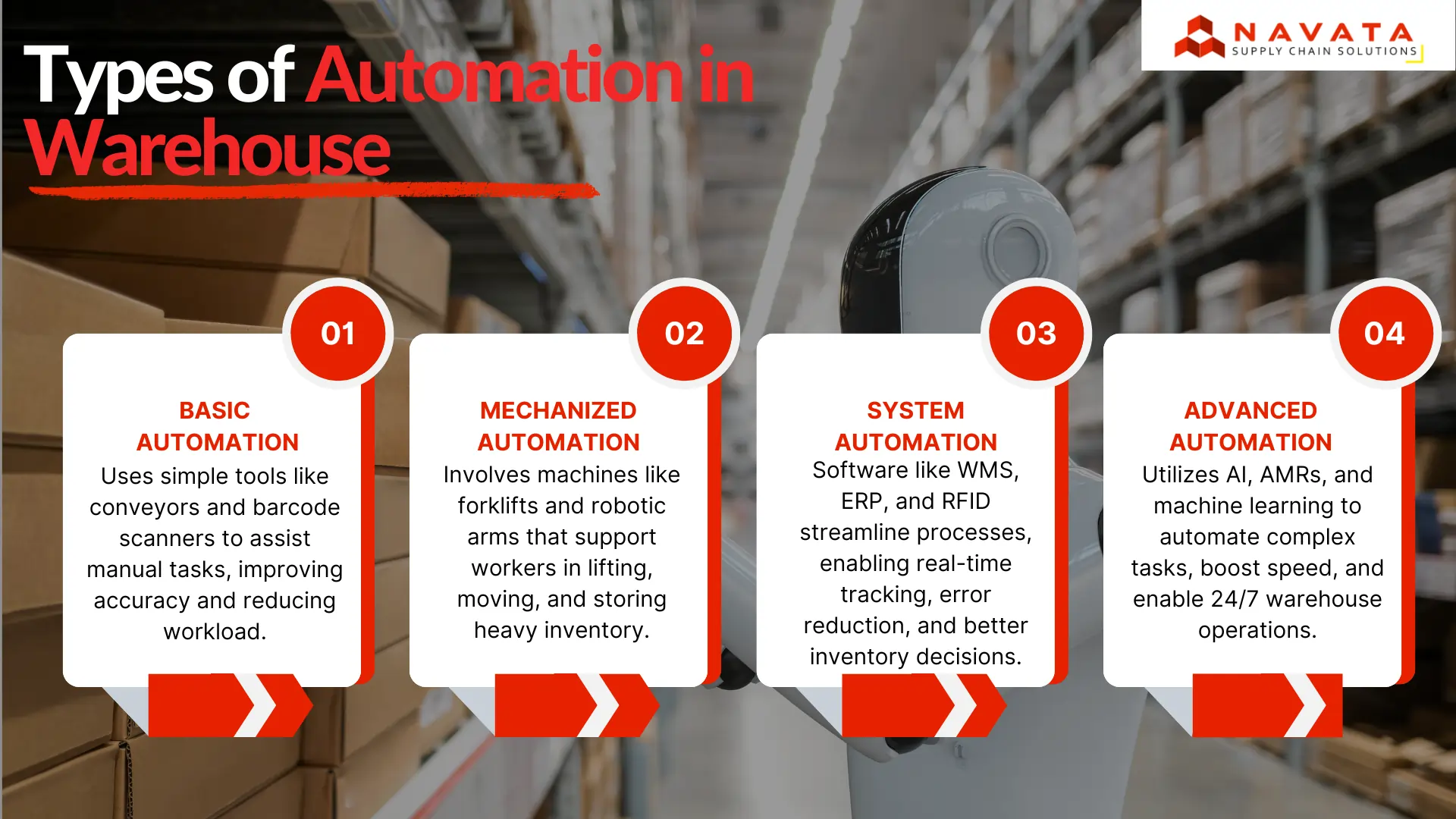
Types of Automation in Warehouse
Basic Automation
Basic automation refers to equipment and machines that help workers do basic, repetitive tasks. Examples include conveyor belts that transport goods from one station to another, barcode scanners for tracking inventory, and pick-to-light systems that use lights to direct workers to pick the right items. These are the tools that work together and not on their own but provide speed and accuracy to the manual process. Basic automation relieves human labor, decreases the likelihood of human error, and ensures productivity is maintained without the necessity for an entire redevelopment of warehouse infrastructure or processes.
Mechanized Automation
In mechanized automation machinery is used to support human labor, which helps to speed up processes and minimizes the time required for intensive work. These include devices such as forklifts, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), robotic arms for picking, and carousels. These machines assist workers in accelerating processes, including inventory movement, loading, and unloading. Mechanized automation aids companies in achieving more capacity, greater throughput and fewer injuries associated with heavy lifting and repetitive motions.
System Automation
Warehouses rely on software-based automation systems to handle and improve their operation processes. Real-time inventory tracking becomes possible through Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). The inventory management systems help multiple departments operate smoothly while maintaining precise stock counts and decreasing administrative work. The fundamental requirement of system automation helps supply chains achieve real-time visibility, decrease errors, and enhance decision-making capabilities.
Advanced Automation
Organizations using advanced automation connect leading-edge tools comprising artificial intelligence (AI) tools with machine learning functions alongside autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). Through their complex capabilities these systems optimize dynamic routes along with conducting real-time inventory assessments and doing complete automated picking tasks and packaging sequences. The autonomous vehicle system operates independently and AI algorithms both control demand forecasting and workflow operations. The advanced automation system decreases human interaction while making operations scalable and permits warehouses to run round-the-clock without significant human oversight to fulfil high-speed order requirements.
Tools and Systems in Warehouse Automation
Software Automation
Modern warehouse operations require the essential software component of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). Real-time management of inventory order processing and workforce tasks is handled by these systems. These systems monitor inventory movements while providing optimised picking directions, which results in error-free operations that enhance supply chain operation efficiency.
Barcode Scanning and RFID
The automation of data entry becomes possible through barcode scanners and RFID systems which extract product information automatically. The item scanning process eliminates errors in record updates because workers perform the scans automatically. RFID tags operate remotely while reading multiple tags at once, which leads to improved inventory accuracy and enhanced visibility and substantial speedups of inbound and outbound procedures.
Automated Conveyors
The warehouse utilises automated conveyor systems to transport products without any human contact. The system transports items between various stations as well as storage facilities at high speed. The implementation of these systems minimises work time while decreasing physical worker strain and enables continuous flow operations, which results in quicker warehouse processes and reduced dependence on manual labour for internal transportation needs.
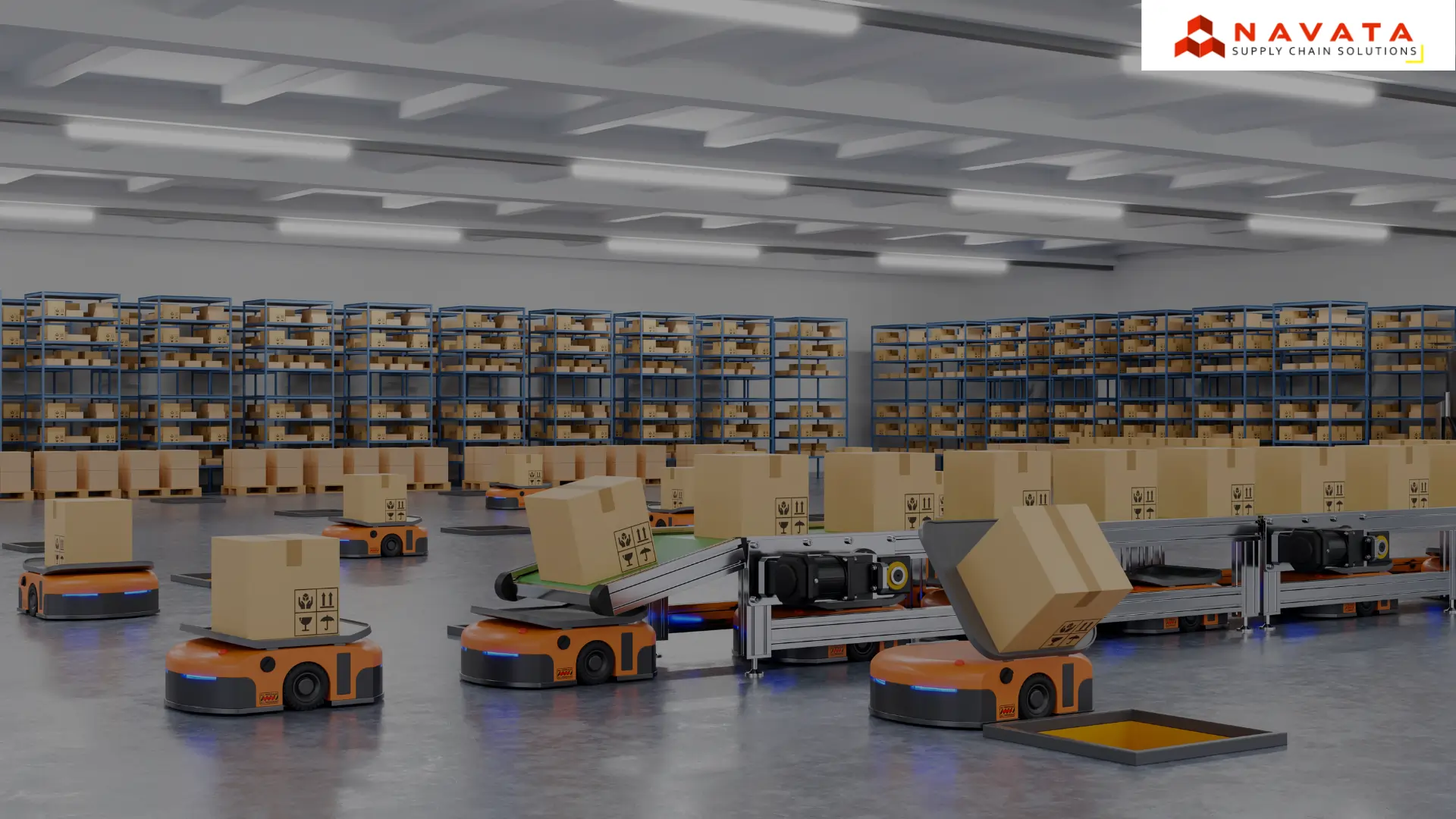
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Warehouse personnel use AGVs as robotic carts that follow programmed routes inside the facility. The machines carry merchandise between storage spaces and picking or packing areas. The operation of AGVs requires minimal human intervention, which leads to reduced labor expenses and safer conditions through restricted forklift usage while delivering consistent operational results for high-throughput environments.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
The navigation system of AMRs depends on sensors and cameras and AI technology to perform dynamic movements in the environment. These robots steer through their surroundings while generating their own best routes independent of predefined routes. AMRs combine their ability to pick up items with their station delivery function in order to increase both flexibility and efficiency. The technology functions optimally in operation areas that undergo quick task and layout adjustments.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
The high-density storage system AS/RS comes fitted with robotic shuttles or cranes that provide automatic item storage and retrieval services. The vertical storage approach within these systems enables maximum space utilisation while simultaneously decreasing the time needed for picking operations. The installation of AS/RS parameters provides precise inventory management with reduced item damage and suits operations that deal with storage quantities followed by rapid item pickup.
Sorting and Packing Automation
Automated sorting systems evaluate items using sensors in combination with software to conduct size-based, weight-based, or destination-based sorting operations. The systems use automated routes to deliver packages to their appropriate shipping destinations. Advanced systems can perform packaging duties, which include placing products in boxes and adding labels, seals, and weights, thus minimising human involvement during order fulfilment.
Here is Your Automated Warehouse, Lets Start!
Warehouse Automation Best Practices Before Starting
Set Clear Goals
Begin by defining the specific problems you want automation to resolve such as speed and accuracy and reducing labour costs. Having clear objectives leads to selecting proper tools alongside providing success measurement methods. When goals remain undefined, automation tends to generate inefficiency instead of achieving efficiency and improvement.
Start Small and Scale Gradually
Don’t automate everything at once. You should start with basic automation tools which include conveyors as well as barcode scanning technologies. Your business should implement advanced systems after basic operational technologies achieve full stability. The approach of phase implementation helps prevent disturbances while enabling team members to adapt and enables assessment prior to additional resource investments.
Choose the Right Technology
Your warehouse automation selection should match its unique requirements which include dimensions and floor plan and order difficulty and financial capacity. The implementation of fancy technological equipment that fails to enhance operational value must be avoided. Your tailored system investment maximizes returns, therefore enhancing operational results without introducing unnecessary complexity.
Train Your Workforce
The implementation of automation systems gives staff members additional capabilities. Your staff needs training to efficiently operate systems alongside proper handling of automated equipment and technical system management. Your team becomes both efficient and safe, and automation succeeds better when employees receive proper training.

Conclusion
Warehouse automation has become an essential strategy for modern supply chain operations, enabling businesses to achieve greater speed, accuracy, and efficiency. By integrating technologies ranging from basic conveyors and barcode scanners to advanced robotics and AI-driven systems, warehouses can reduce manual labor, improve safety, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Implementing automation not only streamlines daily processes but also provides scalability for future growth. With clearly defined goals, the right technology, and proper workforce training, companies can maximize the benefits of automation. Ultimately, automation empowers warehouses to stay competitive in a fast-paced market while delivering reliable, cost-effective, and high-quality services.
Thanks For Reading: What is Warehouse Automation?
Powered By 360Presence