Smart Sensors & Fleet Management
Fleet management is evolving rapidly with the adoption of smart sensors — IoT-enabled devices that continuously monitor vehicle health, driver behavior, and environmental conditions. By collecting real-time data, these sensors empower logistics operators to reduce operational costs, prevent downtime, improve safety, and optimize routes.
In an industry where efficiency and safety are critical, smart sensors serve as the digital nervous system of modern fleets, enabling predictive decision-making and data-driven operations across trucks, buses, and delivery vehicles.

Read More About- Power of Data and Analytics in Supply Chain Management
What Are Smart Sensors in Fleet Management?
Smart sensors are specialized devices that detect, process, and transmit data on vehicle performance, driver behavior, and external conditions. Integrated with telemetry systems, IoT platforms, and fleet management software, these sensors allow fleet managers to monitor assets remotely, identify issues early, and optimize operations.
Key types of sensors include:
Temperature Sensors: Monitor engine, cargo, or refrigerated transport conditions.
Tire Pressure Sensors: Prevent blowouts and improve fuel efficiency.
Fuel Sensors: Track consumption patterns and detect leaks.
GPS and Telematics Sensors: Provide real-time location and route tracking.
Accelerometers & Gyroscopes: Measure sudden braking, acceleration, or tilt.
OBD-II Sensors: Monitor engine diagnostics and fault codes.
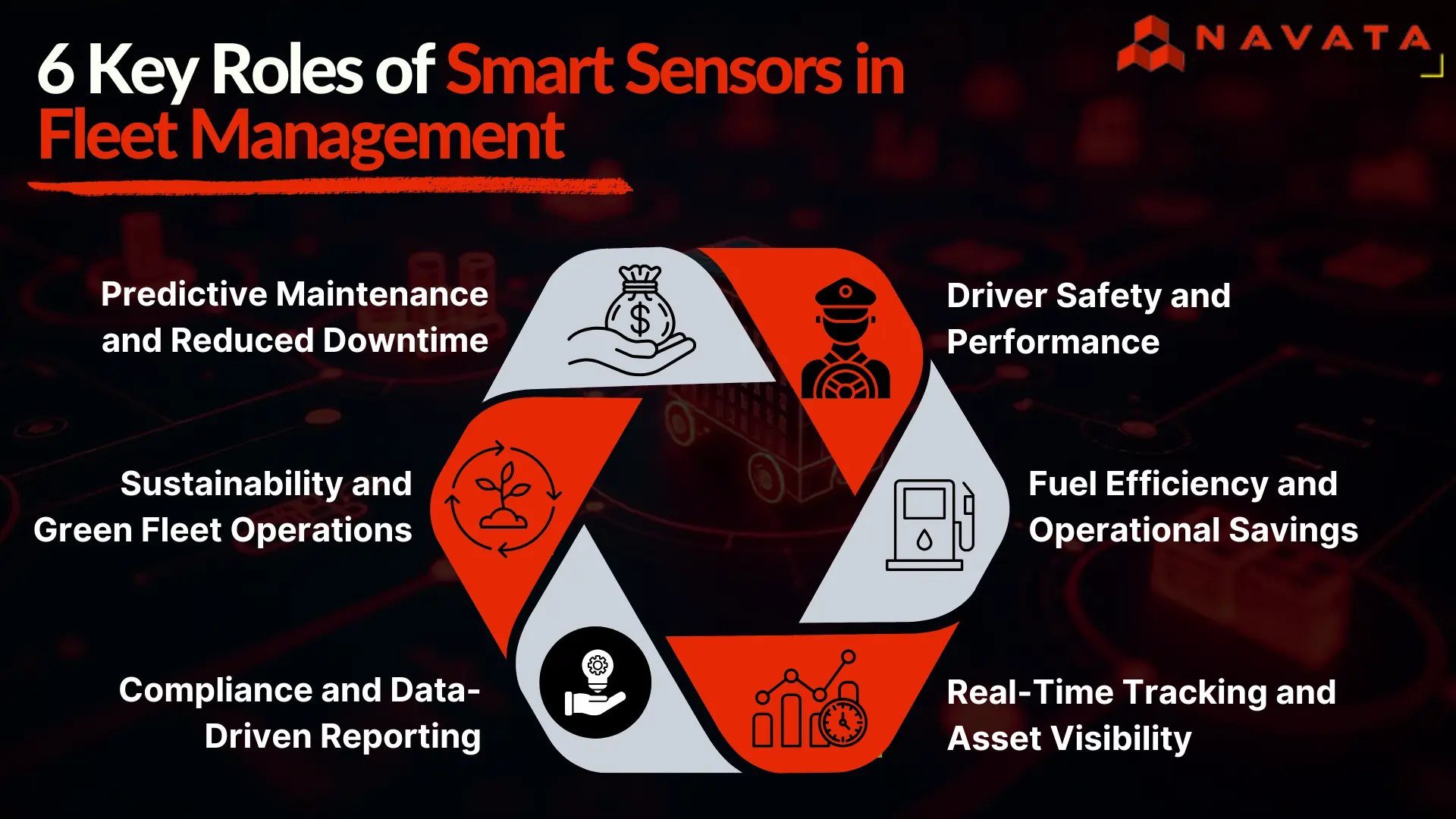
Key Roles of Smart Sensors in Fleet Management
1. Predictive Maintenance and Reduced Downtime
Smart sensors continuously track engine performance, fluid levels, tire pressure, and battery health.
Alerts for anomalies before failures occur
Automated maintenance scheduling
Reduces costly emergency repairs
Result: Higher fleet availability, extended vehicle lifespan, and lower maintenance costs.
2. Enhanced Driver Safety and Performance
Sensors monitor driver behavior such as harsh braking, rapid acceleration, fatigue, and lane deviations.
Real-time alerts improve reaction time
Driver scoring systems encourage safer behavior
Supports regulatory compliance
Result: Safer roads, lower insurance premiums, and a culture of accountability.
3. Fuel Efficiency and Operational Savings
Fuel sensors combined with telematics allow fleet managers to:
Identify inefficient driving habits (idling, over-speeding)
Optimize routes for fuel and time savings
Track vehicle consumption trends over time
Result: Lower operational costs and reduced carbon footprint.
4. Real-Time Tracking and Asset Visibility
Smart sensors integrated with GPS and IoT networks provide continuous location and health monitoring.
Detect route deviations and delays instantly
Monitor temperature, vibration, and load conditions for sensitive cargo
Improve supply chain transparency and client trust
Result: Increased operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and accountability.
5. Compliance and Data-Driven Reporting
Sensors automate the collection of regulatory data such as:
Driver hours and vehicle inspections
Emissions and environmental standards
Maintenance logs and safety audits
Result: Reduced paperwork, lower risk of violations, and easier audit preparation.
6. Sustainability and Green Fleet Operations
By tracking fuel use, idling, and route efficiency, sensors contribute to eco-friendly logistics practices.
Support EV fleet management and hybrid vehicles
Reduce CO₂ emissions through optimized operations
Align with corporate ESG initiatives
Result: Cost-efficient, sustainable, and environmentally responsible fleet operations.
Learn About- Advanced Warehousing Technologies
Future Trends: Smart Sensors and AI in Fleet Management
As fleet operations become increasingly complex and technology-driven, the role of smart sensors integrated with AI and cloud platforms is set to expand dramatically. Emerging trends are not only enhancing efficiency and safety but also enabling predictive, autonomous, and fully connected fleet ecosystems.
AI-Powered Predictive Analytics: Anticipates maintenance needs and optimizes routes dynamically.
Autonomous Vehicle Integration: Smart sensors will serve as the primary perception layer for AVs.
Connected Fleet Ecosystems: Cloud-based platforms will centralize sensor data, enabling global visibility and decision-making.
Fleets that adopt AI-integrated sensors will lead in efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Conclusion
Smart sensors are no longer optional — they are essential for modern, competitive fleet management. By delivering real-time insights, predictive maintenance, driver safety monitoring, and operational efficiency, these devices transform traditional fleets into intelligent, data-driven networks.
For logistics operators, embracing smart sensors is the pathway to reduced costs, improved safety, and greener operations, preparing fleets for the demands of a connected, autonomous, and sustainable future.
Thanks For Reading: Role of Smart Sensors in Fleet Management: Enhancing Safety, Efficiency & Sustainability
Powered By 360Presence

