Drone Delivery vs Traditional Transportation
In logistics, businesses are searching for faster, more efficient, and cost-effective ways to deliver goods. One of the biggest questions emerging today is: Should you stick with traditional transportation methods or invest in drone delivery services? With advancements in last-mile delivery technology and changing consumer expectations, this comparison is more relevant than ever.
In this blog, we break down the differences between drone delivery vs traditional tranportation through the lens of cost, speed, and return on investment (ROI). Whether you’re a logistics professional, e-commerce business owner, or tech enthusiast, this guide will help you understand which delivery method could be right for your business.

You May Also Like to Read: Road Transportation vs Rail Transportation
What Is Drone Delivery?
Drone delivery uses unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to transport packages from warehouses or fulfillment centers directly to customers. These drones can fly autonomously or be remotely controlled and are especially useful for last-mile deliveries, where speed and access are crucial.
Companies like Amazon Prime Air, Zipline, and UPS Flight Forward have already started experimenting or implementing autonomous delivery in selected regions, especially for medical supplies, groceries, and small packages.
What Is Traditional Transportation?
Traditional delivery involves the use of trucks, vans, bikes, and other ground vehicles to carry packages. This method has been the backbone of delivery services for decades. It’s reliable, scalable, and familiar to both businesses and consumers.
It’s a well-established model, traditional vs autonomous delivery raises concerns, as traditional systems often face challenges like traffic congestion, fuel costs, driver shortages, and longer delivery times—especially in urban and remote rural areas.
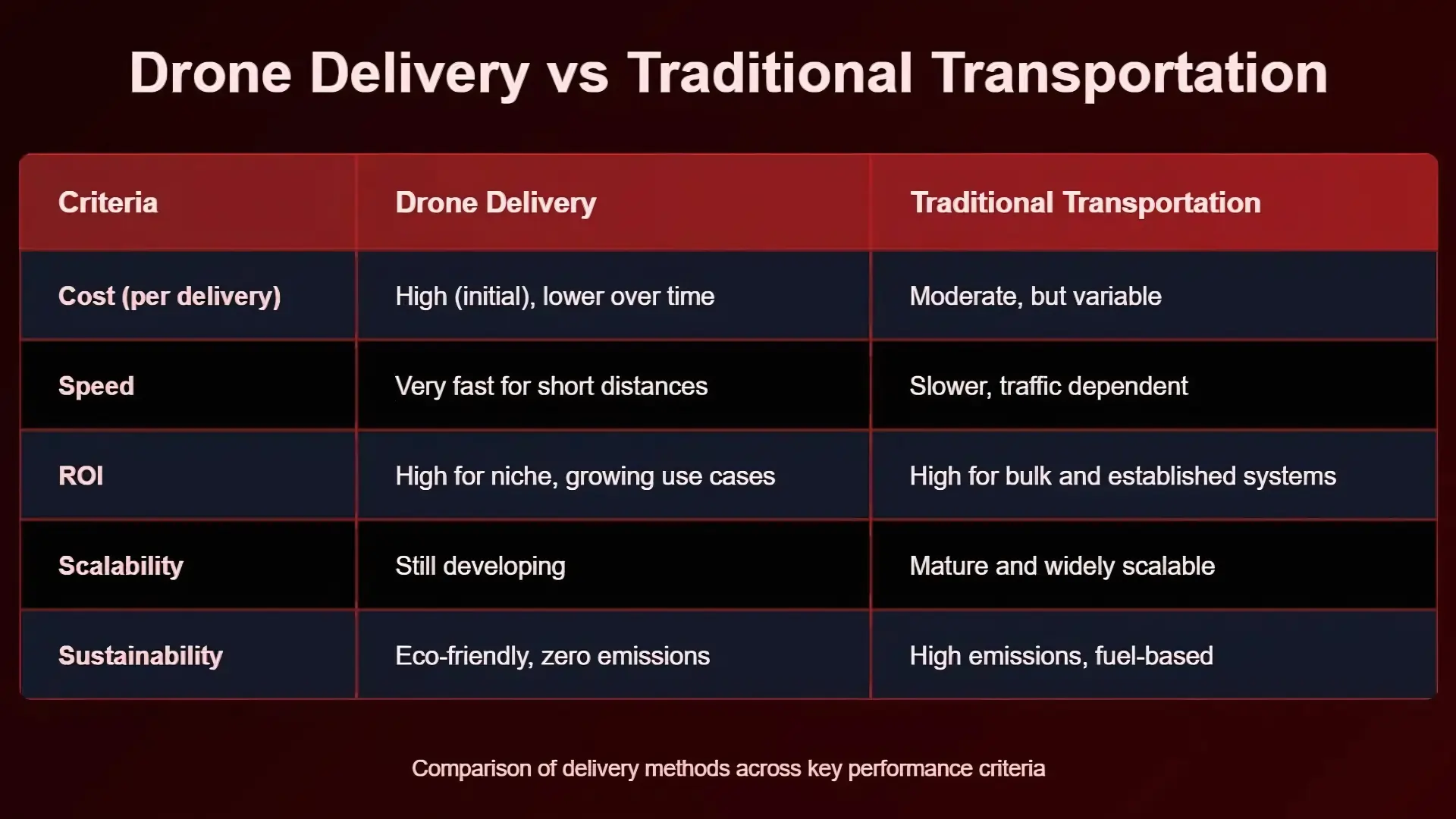
Drone Delivery vs Traditional Transportation: Comparison
1. Cost Comparison
Drone Delivery Cost
The upfront investment in drone delivery is high. You need to account for:
- Drone purchase and maintenance
- Battery charging stations
- Software for navigation and route optimization
- Operator training and licensing
- Insurance and regulatory compliance
According to McKinsey, the cost comparison of drone delivery shows an average of about $13.50 per package in early stages. However, this cost is expected to drop as the technology scales and becomes more efficient. Still, drones are powered by electricity, not fuel—meaning lower variable costs and zero emissions, making them an eco-friendly long-term investment.
Traditional Transportation Cost
Traditional methods are relatively cheaper upfront but come with recurring expenses:
- Fuel and vehicle maintenance
- Driver salaries and training
- Insurance and regulatory fees
- Depreciation of vehicles
Ground delivery costs can range from $5 to $8 per package, depending on distance, vehicle type, and location. While lower on paper, these costs are more variable and can increase with inflation, traffic, or fuel price hikes.
Verdict: Drone delivery has a higher initial cost but may become cheaper over time, especially in dense urban areas or locations with poor road infrastructure. Traditional methods remain cost-effective for bulk deliveries over longer distances.
2. Speed & Efficiency
Drone Delivery Speed
Drones can fly at speeds of 60–90 km/h, often taking direct aerial routes to their destination. This makes them highly efficient in:
- Urban areas with traffic congestion
- Remote regions with poor road access
- Emergency deliveries like medicine or blood samples
Drones also reduce human delays, ensuring more accurate delivery timelines.
Traditional Delivery Speed
Ground vehicles are limited by:
- Traffic conditions
- Road quality
- Driver availability
- Weather disruptions
Average delivery speeds for urban settings are about 25–30 km/h, and routes are often indirect. While bulk delivery is possible, individual parcel speed suffers.
Verdict: Drones in last mile delivery win the speed race in short-range and urgent deliveries, especially in challenging terrains. Traditional transportation remains reliable for scheduled, bulk, and long-haul shipments.
3. Return on Investment (ROI)
Drone Delivery ROI
The benefits of drone delivery services include:
- Reduced labor costs (fewer drivers)
- Faster delivery (better customer satisfaction)
- Lower energy consumption
- Enhanced brand image (green and innovative)
For industries like healthcare, eCommerce, and food delivery, drones can help boost ROI by solving last-mile inefficiencies and enabling same-day delivery services. However, the ROI may take longer due to regulatory barriers, infrastructure needs, and public acceptance concerns.
Traditional Delivery ROI
Traditional transportation excels in:
- High-volume deliveries
- Established supply chains
- Regions with good road infrastructure
- Predictable delivery schedules
Fleet optimization software can further boost ROI by reducing idle time, fuel use, and missed deliveries.
Verdict: Drone ROI shines in niche applications (e.g., medical emergencies, rural logistics). Traditional transport maintains better ROI for general-purpose logistics at scale.
4. Environmental Impact
Drones are battery-powered with zero emissions, aligning with global climate goals. They support sustainable practices and fit into the future of logistics and drone technology.
Traditional ground vehicles—especially diesel-based—contribute to emissions and pollution.
Verdict: Drone delivery is clearly more sustainable and eco-friendly. As regulations tighten around emissions, drone delivery could become not just a preference but a necessity.
You May Also Like to Read: Air Transport vs Rail Transport
Challenges to Consider: Drone Delivery vs Traditional Transportation
For Drones:
- Regulatory restrictions (airspace, weight limits)
- Privacy concerns
- Limited payload capacity
- Weather dependency
- Need for landing infrastructure
For Traditional Methods:
- Traffic congestion
- High fuel costs
- Driver shortages
- Delays and missed deliveries
- Pollution and sustainability issues
Which One Should You Choose?
You May Also Like to Read: Road Transportation Vs Water Transportation
Conclusion
Both drone delivery vs traditional delivery options have strengths. Drones suit fast, last-mile, or emergency deliveries and offer strong ROI in the right conditions. Traditional transport is unbeatable for large volumes and long-distance logistics.
Looking ahead, the future of logistics and drone technology may involve a hybrid model that blends the speed and sustainability of drones with the reliability of ground fleets. Businesses that adopt early stand to gain in efficiency, customer satisfaction, and market reputation.
Thanks For Reading: Drone Delivery Vs Traditional Transportation: Cost, Speed & ROI Analysis
Powered By 360Presence

