Air Transport vs Rail Transport
When it comes to moving goods across regions or countries, two major players dominate the logistics scene: air transport and rail transport. Both have distinct advantages depending on the type of cargo, distance, urgency, and cost.
Whether you’re a business shipping time-sensitive electronics or bulk industrial goods, choosing the right mode of transport directly impacts delivery speed, operational cost, and customer satisfaction. Air and rail transport serve different roles in the supply chain, and understanding when to use each can give your logistics strategy a major edge.
In this blog, we break down the key differences to help you understand which mode of transport is more suitable for your goods transportation needs.

You May Also Like to Read: Road Transportation vs Air Transportation
What is Air and Rail Transport for Goods?
Air transport moves goods by airplanes, making it ideal for fast, long-distance shipping. It’s best for lightweight, high-value, or urgent items like electronics or medical supplies, especially for international deliveries.
Rail transport uses freight trains to move heavy or bulky goods over land. It’s cost-effective for large volumes and is commonly used for domestic or regional shipping. Rail is also eco-friendlier for long-distance overland transport.
What to Choose Air and Rail Transport?
Choosing the right transport mode—air or rail—plays a vital role in how efficiently, safely, and cost-effectively your goods reach their destination. Both modes have unique strengths that suit different types of cargo and business needs.
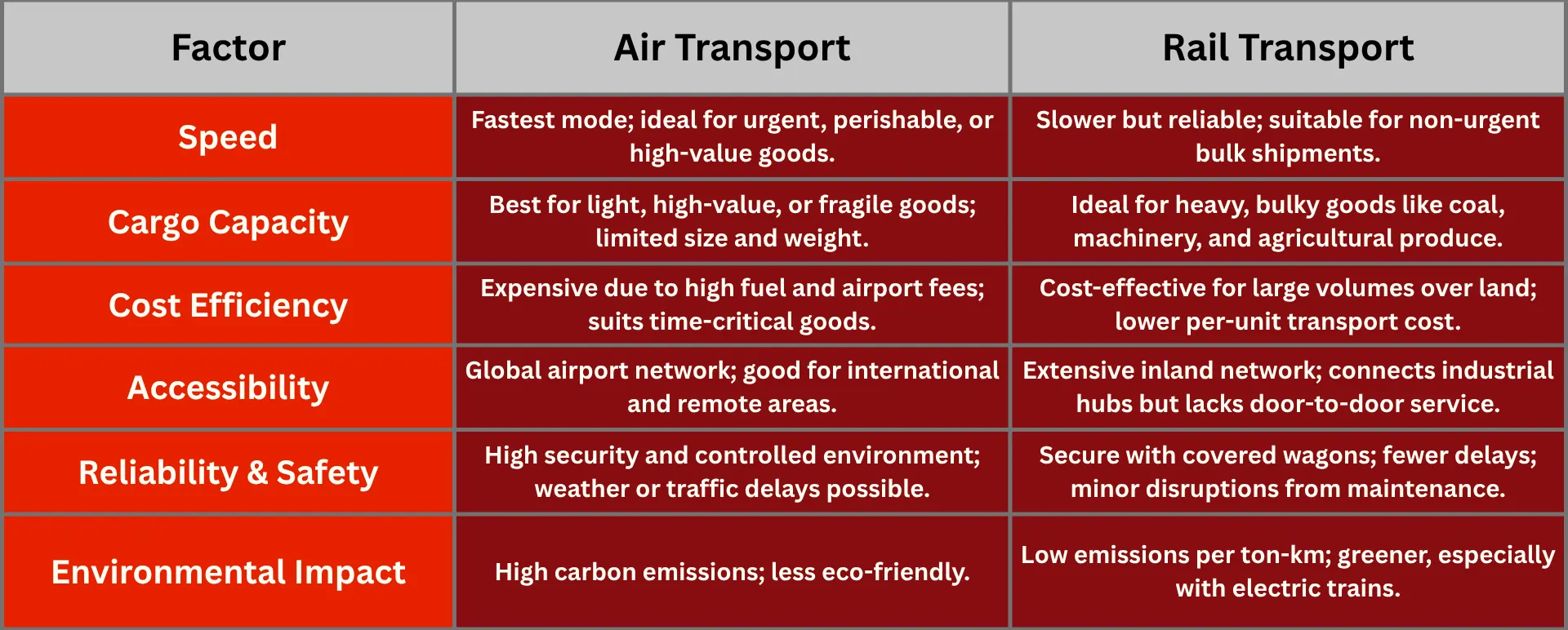
Speed
Air Transport: Air freight is the fastest option for shipping goods. It’s ideal when time is critical, such as for perishable products, urgent medical supplies, or high-value electronics. Airplanes can cover thousands of kilometers in just a few hours, helping businesses meet tight deadlines and reduce inventory holding times.
Rail Transport: Rail is slower compared to air but offers reliable and steady transit times, especially for inland shipments. It is suitable for bulk goods that don’t require immediate delivery. Railways avoid road traffic delays and often run on fixed schedules, making transit times predictable for long distances.
Cargo Capacity and Types
Air Transport: Air cargo is best for smaller, lighter, and often high-value or fragile goods. This includes items like pharmaceuticals, electronics, fashion products, and perishable foods that need quick delivery. However, aircraft have strict size and weight limits, which restricts very large or heavy shipments.
Rail Transport: Railways are built for moving large volumes of heavy and bulky goods such as coal, minerals, machinery, steel, and agricultural produce. Freight trains can haul many wagons loaded with tons of cargo, making rail ideal for heavy industrial shipments over land.
Cost Efficiency
Air Transport: Air freight generally costs more due to high fuel consumption, maintenance, and airport fees. The expense can be worthwhile for businesses that prioritize speed over cost, especially when shipping high-value or time-sensitive goods.
Rail Transport: Rail shipping is often more cost-effective for transporting heavy or bulk goods across long distances on land. Operating costs are lower once infrastructure is in place, and the large capacity of freight trains helps lower the cost per unit of cargo moved.
Accessibility and Network
Air Transport: Air freight benefits from a global network of airports, allowing goods to be shipped internationally and to remote or inaccessible locations such as islands or landlocked regions without rail connections. However, airports are usually located outside city centers, requiring additional ground transport.
Rail Transport: Rail networks cover vast land areas and connect major industrial hubs, ports, and cities, making them highly effective for inland freight. However, trains rarely provide direct door-to-door service, so goods often need trucking for first- or last-mile delivery.
Reliability and Safety
Air Transport: Air cargo follows strict security and safety regulations, with frequent inspections to protect goods during transit. The controlled environment inside aircraft reduces damage and theft risk. Yet, flights can be affected by weather conditions or air traffic delays.
Rail Transport: Railways offer secure and stable transport. Cargo is often carried in covered or locked wagons, shielding goods from weather and theft. The dedicated tracks and scheduled operations reduce accidents and delays, though occasional track maintenance or disruptions can occur.
Environmental Impact
Air Transport: Air freight has a high carbon footprint due to the significant fuel required for flights, contributing heavily to greenhouse gas emissions. While fast, air shipping is less eco-friendly and is usually reserved for urgent deliveries.
Rail Transport: Rail is one of the most environmentally friendly modes for freight transport. Trains emit far less CO2 per ton-kilometer compared to planes and trucks. Electric trains powered by renewable energy further reduce environmental impact, making rail a sustainable choice for heavy and bulk shipments.
You May Also Like to Read: Road Transportation vs Rail Transportation
Conclusion
Both air and rail transport serve vital roles in shipping goods efficiently. Air transport stands out for its speed and global connectivity, making it ideal for urgent or high-value shipments. Rail transport, meanwhile, offers a more affordable and reliable solution for moving heavy or bulk goods across land.
Choosing the right mode depends on your cargo’s urgency, size, destination, and budget. In many cases, businesses benefit from using both modes together, ensuring a balance of speed, cost-efficiency, and reach. Making the right transport decision helps streamline supply chains and improve overall logistics performance.
Thanks For Reading: Air Transport vs Rail Transport for Goods Transport: Which Is Better?
Powered By 360Presence