What Are Logistics Hubs?
Logistics hubs in modern supply chains helps in streamlining operations, reducing costs, and boosting efficiency. Understanding their role is crucial for businesses aiming for optimized logistics. In today’s economy, the movement of goods is more complex and critical than ever.
Businesses constantly seek ways to deliver products faster, more reliably, and at lower costs. This is where logistics hubs come into play. Far more than just simple warehouses, these strategically located logistics centers are dynamic nerve centers that orchestrate the entire flow of goods, from supplier to consumer.
This comprehensive guide will discuss what are logistics hubs, exploring how they function, their essential characteristics, the significant advantages they offer, and key factors to consider when choosing one for your business. We’ll delve into the intricacies of logistics management and how these central points revolutionize goods distribution.

You May ALso Like to Read: What is Multimodal Shipping?
How a Logistics Hub Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
A logistics hub operates like a highly organized machine, ensuring goods move seamlessly through the supply chain. Here’s a look at the typical logistics operations process:
1. Receiving Goods
Products arrive at the logistics hub from manufacturers or suppliers via various transportation modes (air, rail, road). Upon arrival, they are meticulously unloaded and inspected for quality assurance.
2. Organization Within the Warehouse
Once received, goods are strategically stored in modern warehouses, reflecting sophisticated warehousing solutions. This organization considers factors like size, shape, and demand, with items placed on shelves, pallets, or in temperature-controlled zones as needed. Real-time inventory tracking systems are crucial here to prevent issues like overstocking or stockouts.
3. Order Processing
Whenever an order is placed, the designated product is picked by warehouse staff or automated systems. It’s then carefully packaged and accurately labeled with all necessary shipping and logistics information. This is a critical part of the order fulfillment process.
4. Distribution to Destinations
Finally, the packaged product is dispatched to its next destination – whether it’s another hub, a retailer, or directly to the end customer. Goods are loaded onto optimal transport vehicles (trains, trucks, ships, or planes), with advanced software guiding the most efficient routes and GPS tracking ensuring full visibility in logistics.
Characteristics of Logistics Hub
What makes a logistics hub truly effective and a game-changer for businesses? It boils down to several key logistics hub features:
Strategic Location
An exceptional hub boasts seamless connectivity to major transportation networks (airports, seaports, railway terminals, highways). This strategic positioning minimizes transit times and operational costs, often acting as a multimodal logistics park (MMLP).
Advanced Infrastructure
Robust infrastructure for logistics is non-negotiable. This includes spacious warehouses (potentially with temperature-controlled zones for sensitive goods), high-capacity cargo handling equipment (cranes, conveyors, robotics), 24-hour security, and efficient loading/unloading facilities. This defines the quality of advanced warehouse infrastructure.
Technology Integration
Modern logistics hubs are powered by cutting-edge logistics technology. Automation tools, real-time trucking tracking systems, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and data analytics ensure smooth workflows, complete visibility, and optimized decision-making at every stage. This is key to logistics automation.
Value-Added Services
Beyond basic storage and distribution, ideal hubs offer a range of value-added logistics services. These can include packaging, labeling, kitting, light assembly, and robust reverse logistics (handling returns), transforming them into comprehensive, one-stop solutions for businesses.
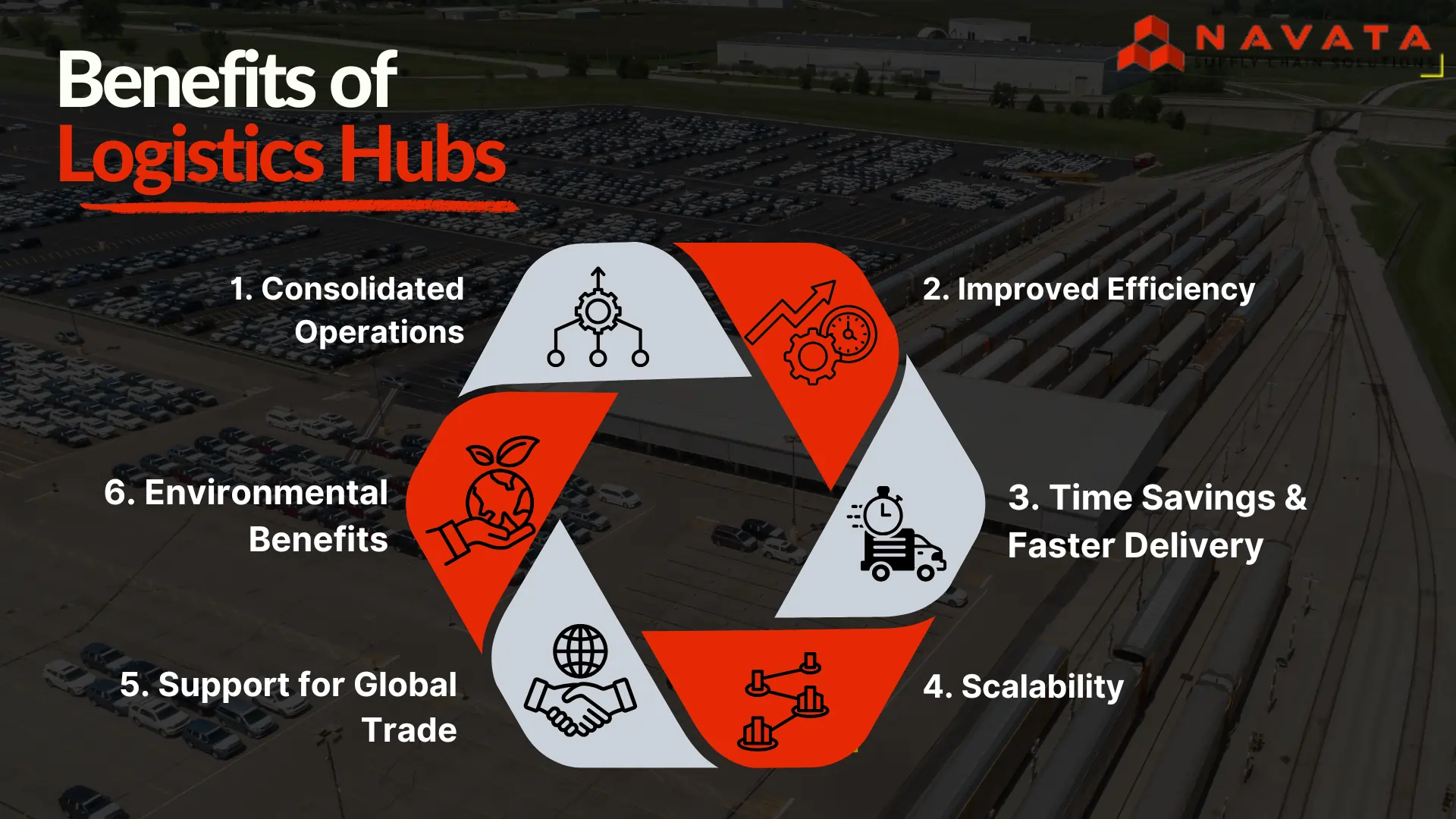
Benefits of Logistics Hubs
The benefits of using logistics hubs into your supply chain are far-reaching and impactful:
Consolidated Operations
By centralizing storage, packaging, and distribution, logistics hubs simplify complex supply chain management. Businesses avoid the need for multiple 3PL warehouses, gaining a unified view and control.
Improved Efficiency
Equipped with the latest logistics technology such as warehouse management systems (WMS), inventory management systems, and route optimization software, hubs significantly enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
Time Savings & Faster Delivery
Their prime connectivity to various transportation modes, such as rail, road, and air, enables quicker delivery to customers and faster delivery times, boosting satisfaction and enhancing brand reputation. Efficient cross-docking facilities further expedite delivery.
Scalability
Designed to handle large volumes of goods, logistics hubs offer inherent logistics scalability, making them perfect partners for growing businesses with fluctuating demands.
Support for Global Trade
For international businesses, customs-bonded warehouses and streamlined documentation processes within hubs facilitate hassle-free import and export, simplifying global trade facilitation for companies of all sizes.
Environmental Benefits
By consolidating goods for bulk and B2B transportation, logistics hubs reduce the number of individual trucks running on the road, leading to fewer carbon emissions. They also support cost-effective LTL (Less Than Truckload) and PTL (Partial Truckload) services, further optimizing freight logistics and providing environmental logistics benefits.
You May Also Like to Read: LTL VS PTL: Difference Between Less Than Truckload and Partial Truckload
Factors to Consider While Choosing a Logistics Hub
Selecting the right logistics hub is a strategic decision that can significantly impact your business’s success. Keep these logistics hub selection factors in mind:
Geographical Location
Prioritize hubs with excellent connections to major transportation networks (sea, rail, airports, highways). Multimodal transport options are key to reducing transit time and costs. This is a crucial logistics location factor.
Advanced Infrastructure
Assess the efficient infrastructure meticulously. Look for capabilities like temperature-controlled storage for sensitive goods, 24-hour security, and modern equipment (cranes, conveyors, robotics) for efficient handling.
Cost Considerations Transparent pricing is vital. Understand all involved costs, including warehousing costs, loading/unloading charges, and transportation expenses, to ensure alignment with your budget. This includes logistics cost reduction strategies.
Regulatory Environment
An ideal logistics hub operates within a business-friendly regulatory environment, offering streamlined customs clearance processes, particularly important for international trade.
Understanding Different Types of Logistics Centers in eCommerce
While often used interchangeably, various types of logistics centers serve distinct functions within the eCommerce landscape:
1. Fulfillment Centers
These are comprehensive logistics centers, often managed by 3PL companies, handling storage, picking, packing, and dispatch. They are equipped with advanced WMS and automation, often part of nationwide networks for optimized last-mile delivery operations.
2. Distribution Hubs
Primarily transit points, distribution hubs consolidate and distribute inventory to its final destination, which could be another fulfillment center, a retail store, or directly for last-mile delivery. They typically offer fewer value-added services.
3. On-Demand Warehouses
Offering flexible, temporary storage solutions, these are ideal for businesses with seasonal products or those needing short-term space. They provide cost-effective options but require careful consideration of consistency.
4. Dark Stores
Also known as micro-fulfillment centers, dark stores are retail spaces repurposed for online order fulfillment. Located in close proximity to customers, they are excellent for fast delivery of perishable goods and cater to local demand.
5. Processing Centers
Similar to distribution hubs but with enhanced capabilities, processing centers handle specialized goods (e.g., fresh seafood), assembly, installation, and offer value-added features like temperature-controlled or dust-proof storage. They blend distribution with light manufacturing processes.
Key Components of a Logistics Hub
Regardless of type, most logistics hub share core components that enable their operations:
Shipping Terminals
These terminals are generally equipped with heavy machinery such as cranes and forklifts to lift and load items onto transit vehicles. This is an important component for efficient goods handling.
Intermodal Dispatch Points
This aspect of a logistics hub is responsible for loading, unloading, and transporting products by different means such as air, road, rail, or sea, showcasing true multimodal transport capabilities.
Last-Mile Transport Hubs
They act as smaller distribution hubs and are designed to cater to fulfill orders to local areas, critical for last-mile delivery.

You May Also Like to Read: Role of Skilled Workers in Successful Supply Chain
Conclusion
So, what are logistics hubs? They are absolutely central for running supply chains efficiently and affordably. By bringing operations together in one place, using advanced logistics technology, and offering many different logistics services, these hubs give businesses the power to meet customer needs, grow worldwide, and gain huge advantages over competitors.
Understanding their detailed workings and picking the right partners—especially those with wide networks of logistics centers—can really change the game for today’s brands. This is vital for those aiming for delivery speeds like major e-commerce players and seamless e-commerce logistics.
Thanks For Reading: What Are Logistics Hubs? Your Guide to Their Role, Benefits & Types
Powered By 360Presence


4 Comments
Comments are closed.