Last-Mile Delivery Problem in India
India’s logistics ecosystem has evolved rapidly with the surge in e-commerce, quick commerce, and on-demand delivery. Yet, last-mile delivery — the final stage of moving a product from a local hub to the customer’s doorstep — remains the most inefficient and cost-intensive link in the supply chain.
In Indian cities, where traffic congestion, inconsistent addressing, and fragmented logistics networks are daily hurdles, last-mile delivery can consume up to 53% of total supply chain costs. Solving this challenge is crucial not just for logistics players but also for retailers, D2C brands, and eCommerce platforms seeking to scale profitably.
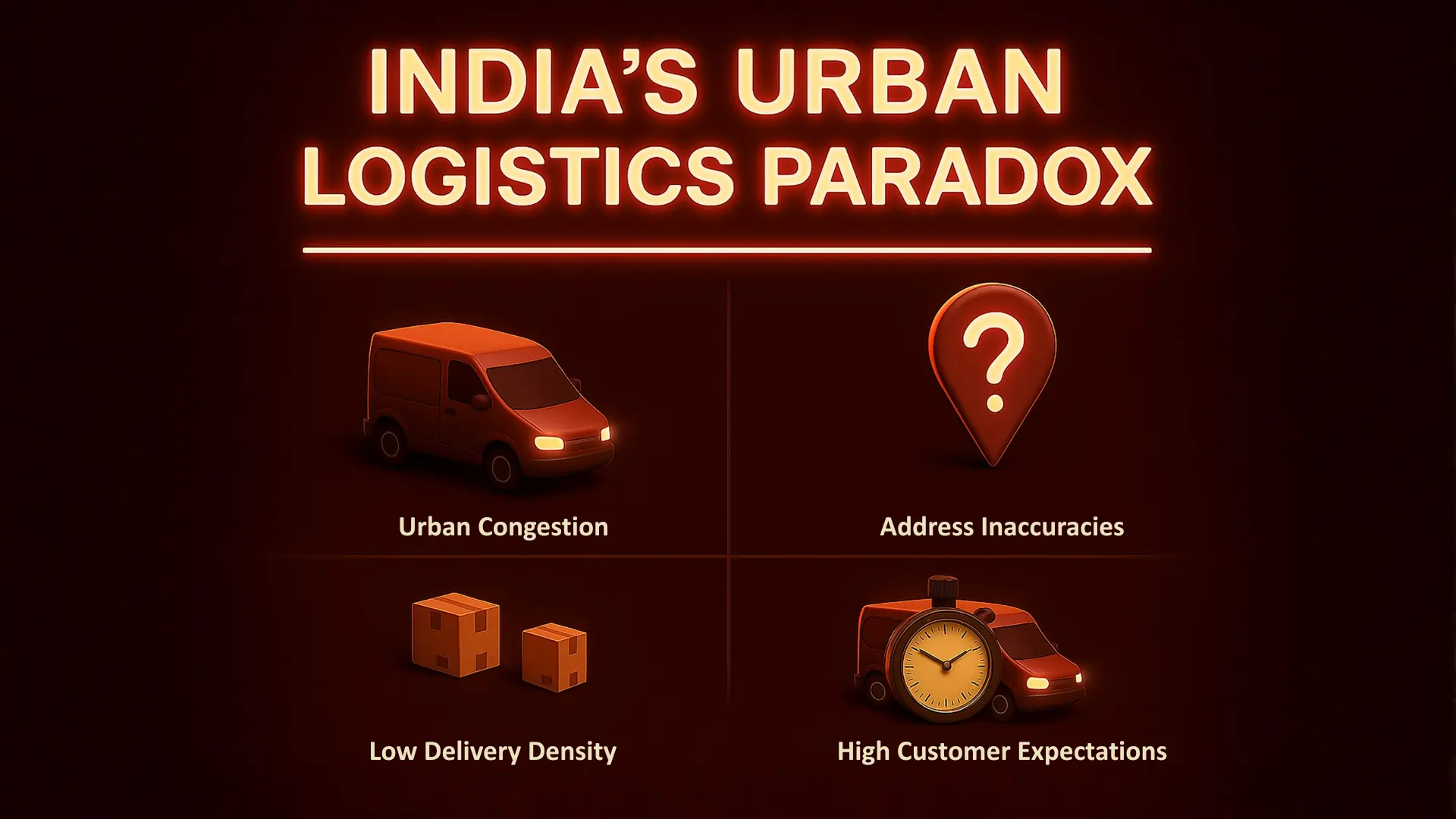
Why Last-Mile Delivery Is So Difficult in Indian Cities
Unlike developed nations with structured postal codes and smooth urban logistics, India’s cities present a unique operational paradox — massive demand concentrated in complex, congested geographies.
Key Structural Challenges
Urban congestion: A 2024 TomTom report ranks Bengaluru and Mumbai among the world’s top 10 most congested cities. Delivery vehicles often spend 30–40% of route time idling in traffic.
Address inaccuracies: India lacks a standardized addressing system. About 20% of last-mile delays are due to incorrect or incomplete addresses, especially in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities.
Low delivery density: Fragmented orders (especially in quick commerce and groceries) make per-drop cost unviable.
High customer expectations: The “Amazon effect” has normalized same-day or 2-hour delivery, forcing logistics providers to balance speed with profitability.
These issues multiply operational costs and make scaling difficult without innovation.
The Cost Dynamics Behind Last-Mile Inefficiency
Every kilometer closer to the customer increases cost non-linearly. According to industry data:
Fuel and labor costs rise by up to 25% during peak traffic hours.
Failed or rescheduled deliveries account for 8–10% of total delivery expenses.
Manual route planning leads to 10–15% higher mileage compared to optimized routing.
Hence, improving last-mile efficiency isn’t just about logistics — it’s about data precision, network design, and technology adoption.
Optimize Your Last-Mile Delivery with Experts!
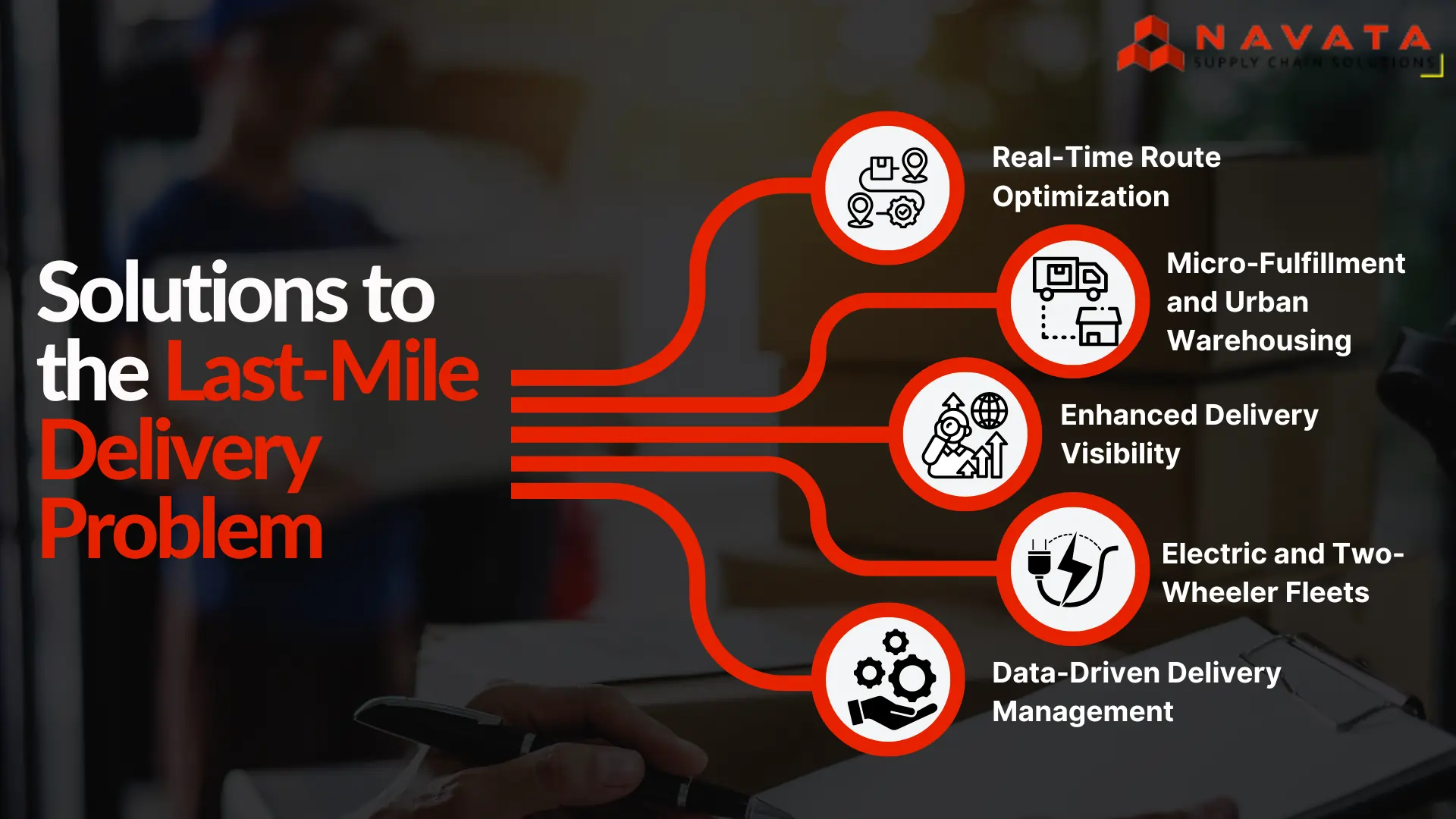
Proven Solutions to the Last-Mile Delivery Problem
a. Real-Time Route Optimization
Advanced route optimization systems leverage AI and GPS analytics to plan the most efficient delivery paths.
They analyze live traffic, weather, and delivery density to dynamically adjust routes.
Businesses adopting real-time routing see up to 30% faster deliveries and significant fuel savings.
Dynamic routing transforms delivery from reactive to predictive — minimizing time and operational cost.
b. Micro-Fulfillment and Urban Warehousing
Traditional central warehousing is no longer efficient for city deliveries.
Micro-warehouses — small urban hubs located closer to high-demand areas — enable faster fulfillment and reduce travel distance.
They can shorten last-mile routes by 40–60%, improving delivery speed and flexibility.
They support hyperlocal and same-day delivery models in dense metropolitan zones.
This distributed storage strategy is particularly effective in India’s Tier-1 and Tier-2 cities where quick accessibility is key.
c. Enhanced Delivery Visibility
Real-time visibility is essential to maintaining delivery reliability and customer trust.
IoT sensors and GPS tracking allow continuous vehicle and shipment monitoring.
Electronic Proof of Delivery (ePOD) ensures instant confirmation and reduces paperwork.
Customer tracking dashboards enhance transparency, reducing complaints and failed deliveries.
Visibility not only improves accountability but also provides valuable data for future performance optimization.
d. Electric and Two-Wheeler Fleets
The growing adoption of EVs and two-wheelers in logistics addresses both sustainability and efficiency.
EVs lower operational costs by 30–40% per kilometer and eliminate fuel volatility.
Two-wheelers offer better maneuverability in congested urban zones.
Expanding government incentives and charging infrastructure make EV logistics more viable.
Integrating sustainable fleets into last-mile operations cuts emissions and aligns with emerging environmental goals.
e. Data-Driven Delivery Management
Data analytics helps identify performance gaps and predict delivery patterns.
Predictive analytics anticipates peak demand and allocates resources accordingly.
Automated dispatch systems reduce idle time between deliveries.
Geospatial intelligence improves route clustering for maximum delivery density.
By turning data into actionable insights, companies can convert unpredictability into measurable efficiency.
The Road Ahead: What’s Next for Urban Last-Mile Delivery
The next evolution of last-mile delivery in India will be tech-driven, autonomous, and sustainable:
AI-led predictive logistics will dynamically allocate resources based on order inflows and real-time traffic.
Autonomous vehicles and drones will begin to play roles in controlled urban zones.
Sustainability mandates will drive the transition to electric fleets and renewable-powered hubs.
Digital twin simulations will allow logistics planners to model and optimize urban networks virtually before deployment.
These advances will define the future of fast, transparent, and eco-efficient last-mile delivery.
Thanks For Reading: Solving the Last-Mile Delivery Problem in Indian Cities
Powered By 360Presence

