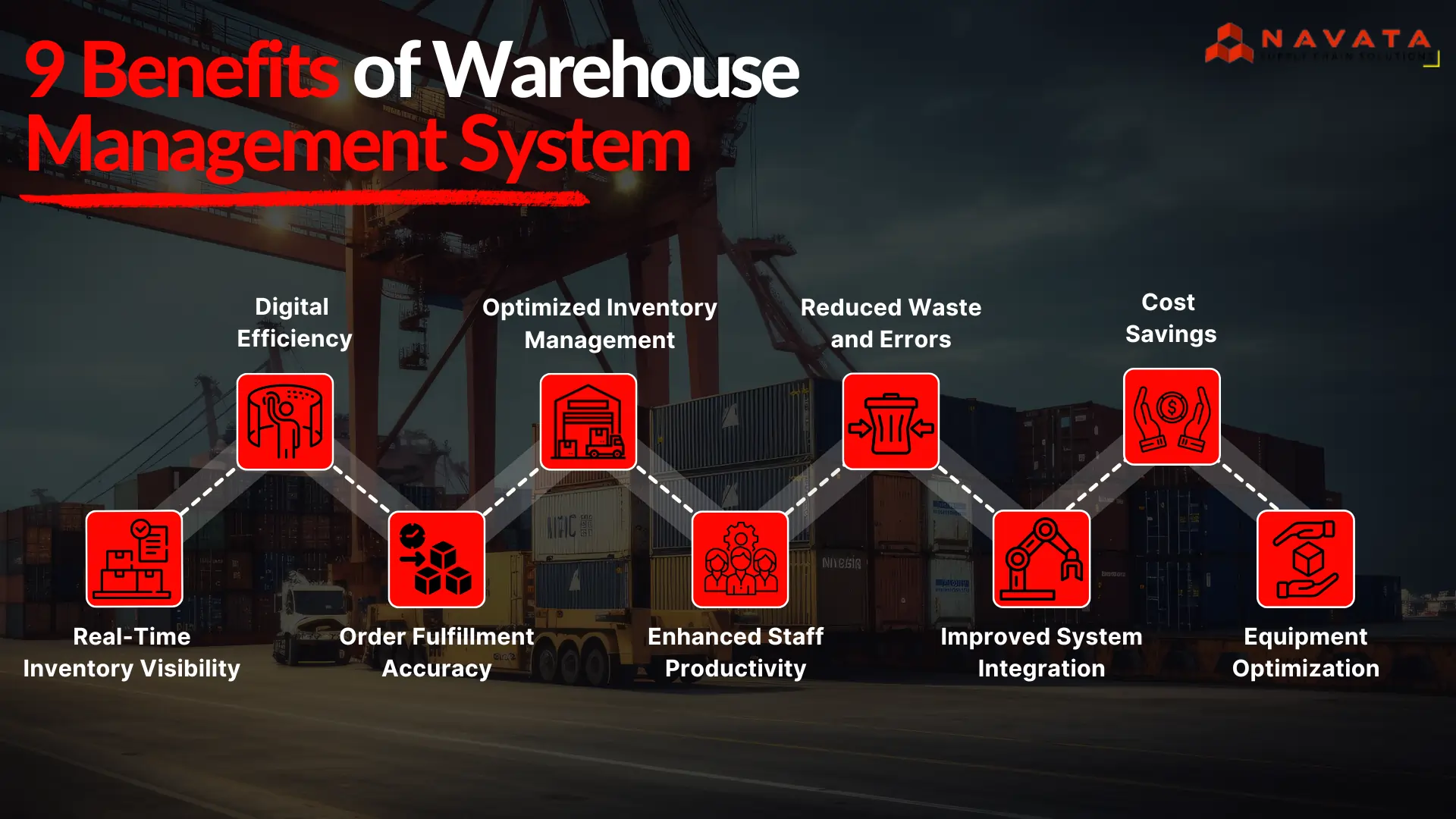
Components of Warehouse Management System
A warehouse management system (WMS) forms the backbone for effective warehouse operations. In a single arrangement, it brings together processes that include inventory management, picking, packing, and shipping. Through technology, WMS maximizes accuracy, speed, and visibility in operations across the supply chain. This blog post elaborates on the inherent components comprising a WMS and how these inherent components play a part in the overall process of driving warehouse performance through effective demand fulfillment for the received customer orders.
A clear understanding of these components is key to businesses looking to streamline their operations and maintain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market environment..

Inventory Management
Inventory management is one of the basic of the WMS applications of an organization. This helps in serving as the most central way through which the movement as well as the storage of the various commodities in the warehouse is followed. Through real-time exposure of actual stock status, WMS provides the business with an actual view of the current stock status. This capability is crucial to avoid stock out situations, and to manage inventory in order to avoid an excessive accumulation of goods, as well as to improve the order delivery rates.
When inventory control is well implemented, stock in various organizations has to be properly dealt with, the costs of holding stock has to be reduced, as well as ensure that the product is available to the consumer when required and this will enhance the effectiveness of the organizations and the satisfaction of consumers.
Order Management
Warehouse management systems are software solutions that help warehouses in managing orders, inventory levels, tracking shipments, and maximizing worker use. Order management is a fundamental component of these systems. Order management in WMS typically includes three functions: order entry, order inquiry, and order execution.
The order input function allows you to enter orders into the system or upload them to the WMS. The order inquiry is used to view an order’s status as well as its audit trail. The order execution function processes orders, assigns them to waves, and assigns selecting and sorting duties.
Order Picking and Packing
The order picking and packing functions of WMS speed up the customer order fulfillment process, reduce errors, and increase productivity. These capabilities allow warehouse employees to pick and pack orders more efficiently by displaying picking lists directly on their mobile devices, directing them to the location of each product, and defining the quantity to pick.
WMS also enables various picking methods, such as picking by item, group, or zone, enabling for efficient order fulfilment that is suited to the warehouse’s and customers’ individual requirements. Furthermore, it guarantees that packing is completed in the proper order and according to customer specifications, resulting in greater customer satisfaction.
Barcode Scanning and RFID
Barcode scanning and RFID in WMS allows for precise and efficient inventory tracking throughout the warehouse. This component contribute to precise inventory tracking and management by improving visibility, speeding up scanning, and increasing data collection accuracy.
Furthermore, unlike barcodes, RFID tags do not require a line-of-sight scan, allowing for faster and more efficient scanning while also providing extensive inventory information.
Cross-docking
WMS cross-docking facilitates the efficient transfer of goods from receiving to shipping, hence minimizing storage requirements. WMS contributes to a leaner supply chain, faster order fulfillment, and lower costs by delivering accurate and timely information and communication between the warehouse management system and the transportation system.
Real-time Inventory
The warehouse management system also includes real-time inventory tracking: A “push” inventory system moves commodities into storage as they are created, regardless of client requests. under contrast, under a “pull” approach, supplies are only removed from storage when a customer order is pending. By reducing delays and increasing efficiency many warehouses are now adopting a push-pull method that incorporates features of both approaches. Real-time inventory tracking is one of the most important features of this system.
By regularly monitoring stock levels warehouse managers can guarantee that products are available when needed by minimizing overstocking and expenses associated to it. In today’s competitive environment, successful warehouse management requires real-time inventory tracking.
You May Also Like to Read: 7 Effective Inventory Management Strategies for Operational Excellence
Shipping and Order Fulfillment
The shipping and receiving module is an essential component of a warehouse management system. This module monitors incoming and departing shipments to ensure that orders are processed correctly and on time. Another important component is the inventory management module.
This module monitors inventory levels, allowing firms to quickly adjust to variations in demand. Businesses that effectively manage these and other aspects of their operations can ensure that orders are completed efficiently and with few errors.
Improve Your Warehouse Operations Today!
Labor Management
Labor management software gives you a real-time snapshot of employee productivity and helps you optimize employment levels. Labor management software can assist enhance warehouse accuracy and efficiency by eliminating the need for manual data entry and tracking.
In addition, labor management software can assist in identifying concerns like as excessive overtime, absenteeism, and turnover. By addressing these challenges, warehouse managers may assist boost staff morale and retention.
Reporting and Analytics
Data-driven insights can automatically offer a roadmap to improvement. WMS creates detailed reporting and analytics on KPIs for things like order accuracy, inventory turnover, and labor productivity that businesses can use to get the ball rolling on pattern spotting, making data-driven decisions and improving warehouse procedures.
Automation
Automation is a very important part of Warehouse Management System used within different technologies, such as barcode scanning, RFID, and AGVs, across various processes for routine tasks like data capture and material movement. This emerging warehouse automation provides data capture to ensure accuracy and real-time inventory tracking, thereby reducing errors and increasing operational efficiency. AGVs automate material movement across a warehouse, increasing throughput while reducing labor costs.
The ability of such seamless integration of automation into a WMS increases not only operational efficiency but also provides the features of scalability and agility that a warehouse needs to meet today’s demands in the dynamic supply chain.
Conclusion
WMS stands as the foundation of proper work in the warehouse; it is a system that consists of components to manage stocks, perform orders, and track ongoing activities. From using bar codes, RFID, AGV or other related systems, WMS directs and supports the tasks in order to increase accuracy and efficiency and cut expenses of workers.
This automation, however, goes hand in hand with the objective of improving the scalability and flexibility required to meet the overall competition in today’s world. Awareness and management of these components are vital for companies those wish to achieve their goal of improving warehouse efficiency and reducing expenses at the same time in the contemporary and rapidly evolving supply chain environment.
Thanks For Reading: Core Components of Warehouse Management System
Powered By 360Presence
FAQ
What are the key component of warehouse management?
The key component of warehouse management maximizes accuracy, speed, and visibility in warehouse operations across the supply chain by managing inventory, picking, packing, and shipping processes.
Why is Mobile Functionality important in a WMS?
Mobile Functionality enables real-time data access and decision-making, enhances flexibility and adaptability, and supports traceability and work order execution through mobile devices.
What role does Inventory Management play in a WMS?
Inventory Management helps track the movement and storage of goods, prevents stockouts, manages inventory levels, and improves order delivery rates.
What is Cross-docking in a WMS and what benefit does it provide?
Cross-docking facilitates the efficient transfer of goods from receiving to shipping, minimizing storage requirements and enhancing order fulfillment speed and efficiency.
What is the job of a freight forwarder?
The job of a freight forwarder is to manage the logistics of shipping goods, including planning transportation routes, coordinating with carriers, handling documentation, ensuring customs compliance, and arranging cargo insurance to facilitate efficient and secure delivery.

2 Comments