What is a Distribution Center?
A distribution center is a specialized facility designed to store, manage, and distribute products efficiently to retailers, wholesalers, or directly to consumers. Unlike conventional warehouses that focus solely on storage, DCs are equipped for high-volume throughput, enabling faster order processing, packaging, cross-docking, and last-mile delivery operations.
Distribution centers play a vital role in:
Reducing lead times between production and delivery
Enhancing order accuracy and speed
Optimizing inventory levels across regions
Supporting omnichannel fulfillment for eCommerce and retail networks
Modern DCs rely heavily on automation, robotics, Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), and data analytics to drive precision and real-time visibility across operations.

Functions of a Distribution Center
A distribution center serves as the operational backbone of modern logistics, ensuring smooth product movement from manufacturers to end users. Its key functions include:
Storage and Inventory Management:
Efficiently stores products while maintaining real-time inventory visibility using Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and automated tracking tools.Order Processing and Fulfillment:
Handles picking, packing, labeling, and dispatching orders accurately to meet delivery timelines and customer expectations.Cross-Docking Operations:
Transfers inbound goods directly to outbound transportation with minimal storage time, reducing costs and speeding up deliveries.Transportation Management:
Coordinates inbound and outbound shipments across multiple carriers and routes, optimizing freight costs and delivery schedules.Quality Control and Inspection:
Ensures products meet quality standards before reaching customers, minimizing returns and improving customer satisfaction.Reverse Logistics:
Manages product returns, repairs, and recycling efficiently to recover value and promote sustainability.
In essence, the functions of a distribution center go beyond storage — they integrate technology, process efficiency, and logistics coordination to keep supply chains responsive and cost-effective.
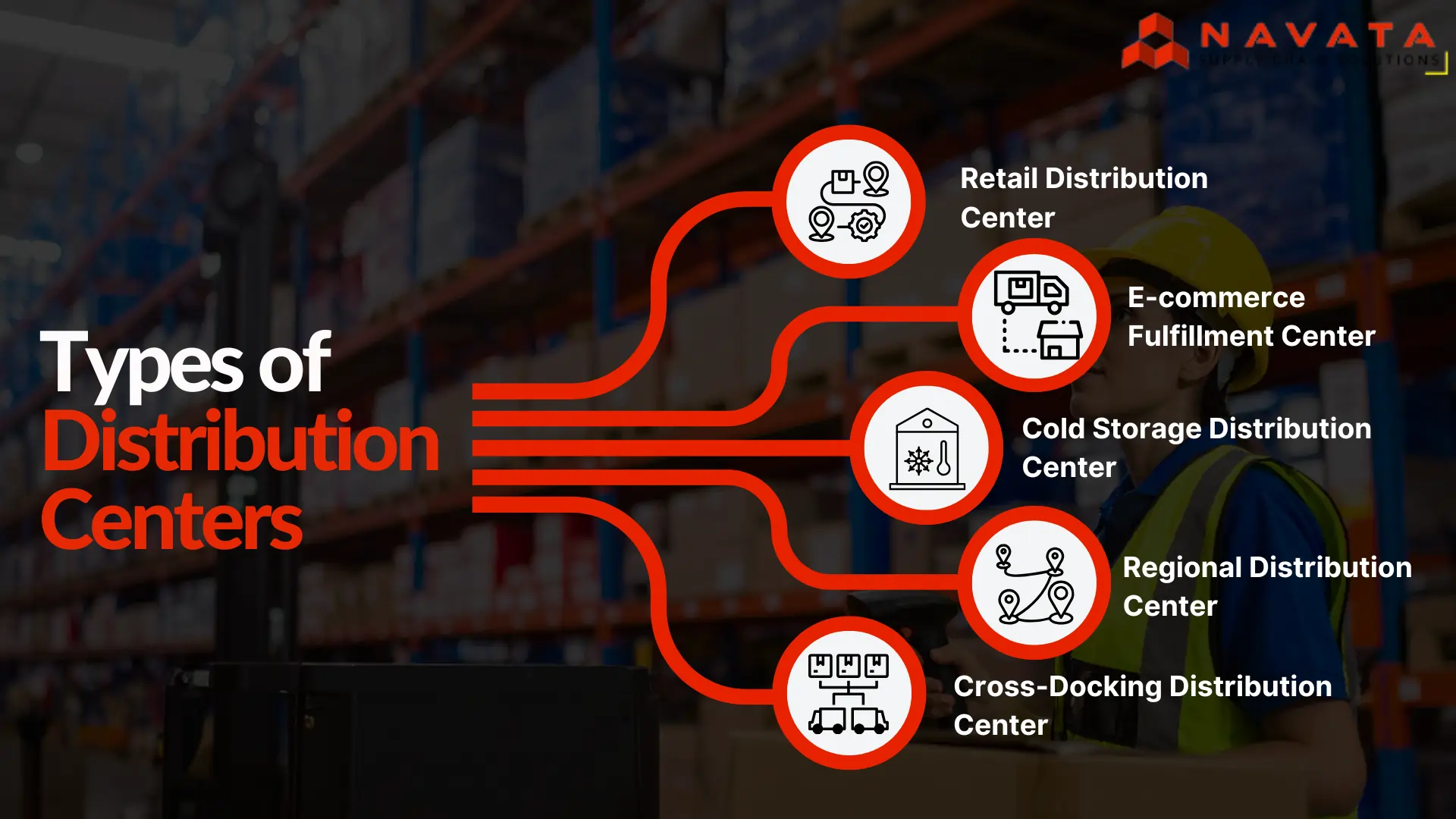
Types of Distribution Centers
Different industries and supply chain models require specialized types of distribution centers. Here are the most common ones:
1. Retail Distribution Center
Designed to supply goods to retail stores or franchise outlets.
Handles large product volumes and frequent replenishments.
Focuses on maintaining consistent stock availability across stores.
Often located near key retail hubs to reduce transit times.
2. E-commerce Fulfillment Center
Tailored for online retail operations with high order frequency and small order sizes.
Supports pick, pack, and ship operations.
Integrates with real-time order management and inventory tracking.
Focuses on fast, accurate deliveries for customer satisfaction.
3. Cold Storage Distribution Center
Used for perishable goods such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
Maintains temperature-controlled environments.
Requires specialized infrastructure and monitoring systems.
Critical for industries with strict compliance and safety standards.
4. Regional Distribution Center
Acts as an intermediate hub between national and local facilities.
Consolidates inbound shipments and redistributes them regionally.
Improves logistics efficiency across large geographical areas.
Often connected to multimodal transport routes (rail, road, sea, air).
5. Cross-Docking Distribution Center
Focuses on speed over storage by minimizing inventory holding.
Products are received, sorted, and dispatched almost immediately.
Ideal for fast-moving goods, perishables, or high-demand items.
Reduces storage costs and accelerates delivery timelines.
Benefits of Distribution Centers
1. Faster Order Fulfillment
Distribution centers streamline the flow of goods from suppliers to customers, cutting down delivery times and enhancing responsiveness.
Consolidates orders and processes them efficiently.
Reduces lead time between order placement and shipment.
Enables faster replenishment for retail and eCommerce.
Result: Improved customer satisfaction and retention.
2. Enhanced Inventory Control
DCs improve inventory accuracy through technology-driven systems that monitor stock levels in real time.
Utilizes WMS, barcode scanning, and RFID for visibility.
Minimizes stockouts and overstocking.
Supports data-driven demand forecasting.
Result: Optimal stock management and reduced working capital.
3. Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
Centralized operations lead to significant cost savings.
Reduces transportation costs through route consolidation.
Optimizes labor and equipment utilization.
Lowers overhead by combining storage and distribution functions.
Result: Greater cost efficiency and higher operational ROI.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
Distribution centers provide the adaptability needed for growth and demand fluctuations.
Expandable layouts and modular systems.
Supports new market entry or product line expansion.
Easily integrates with third-party logistics (3PL) providers.
Result: Seamless scalability without disrupting operations.
5. Technology Integration and Automation
Modern DCs leverage smart technologies to maximize throughput and precision.
Employs robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and AI analytics.
Enables predictive maintenance and real-time tracking.
Improves safety and reduces human error.
Result: Higher productivity and long-term operational sustainability.
6. Improved Supply Chain Visibility
Integration with digital systems gives businesses end-to-end insight into operations.
Real-time monitoring of inbound and outbound shipments.
Data analytics for performance optimization.
Supports transparent communication with partners and customers.
Result: Proactive decision-making and stronger supply chain resilience.

Conclusion
A distribution center is no longer just a storage facility — it is the engine that powers modern supply chains. By integrating technology, visibility, and scalability, DCs enable businesses to deliver faster, operate leaner, and stay competitive in a global marketplace.
As companies focus on customer experience and supply chain agility, investing in efficient distribution center networks is not just a logistical choice — it’s a strategic advantage.
Thanks For Reading: What is a Distribution Center? Types & Benefits!
Powered By 360Presence

