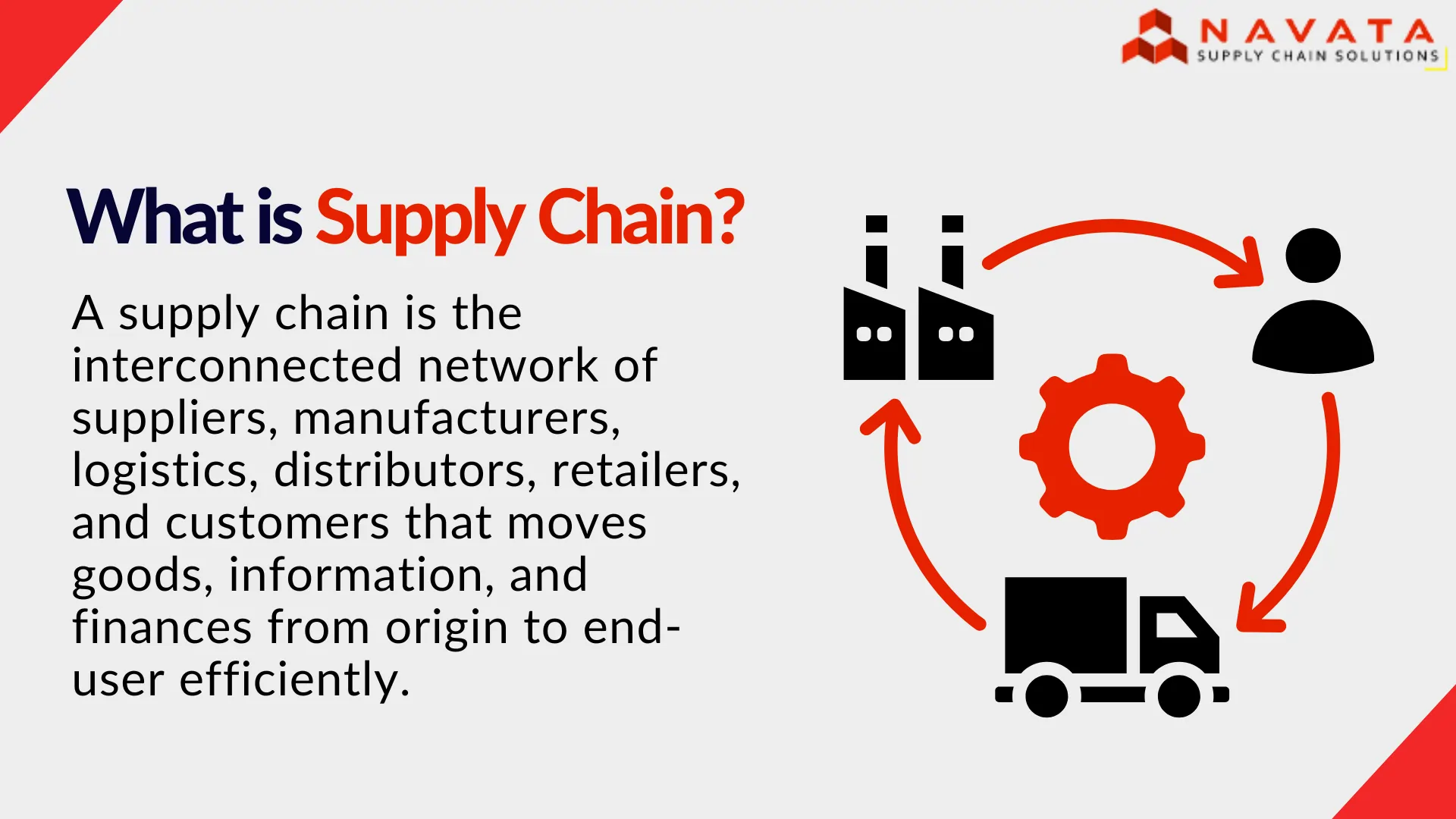
What is Supply Chain?
Every product you use, from electronics to groceries, passes through a supply chain. A supply chain is the system that moves goods efficiently from suppliers to customers while managing costs, timelines, and risks.
A supply chain is the end-to-end network that ensures products or services reach customers efficiently. It manages:
Physical goods flow – Moving raw materials to production facilities and finished products to customers.
Information flow – Tracking orders, forecasts, and shipments to make informed decisions.
Financial flow – Handling payments, invoicing, and cost optimization.
Supply chains are dynamic networks, not linear chains. Decisions in procurement, production, or logistics affect the entire system. Companies that fail to integrate all components often face delays, higher costs, and lower customer satisfaction.
Core Components of a Supply Chain
Understanding the building blocks of a supply chain is crucial:
1. Suppliers
Suppliers provide raw materials or components needed for production. They are the first link in the supply chain, and any disruption at this stage can affect the entire network. Reliable suppliers ensure quality materials reach manufacturers on time.
2. Manufacturers/Producers
Manufacturers transform raw materials into finished products. Their efficiency, capacity, and quality control directly influence timelines, product quality, and customer satisfaction within the supply chain.
3. Logistics and Transportation
Transportation moves goods between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers. Delays or inefficiencies in logistics can create bottlenecks, highlighting the critical role of timely, reliable movement in a supply chain.
4. Distributors and Wholesalers
Distributors and wholesalers bridge the gap between manufacturers and retailers or large buyers. They ensure products are delivered efficiently and in the right quantities, maintaining the flow of goods within the supply chain.
5. Retailers
Retailers are the final commercial point where products reach end consumers. Their coordination with distributors ensures availability, proper stocking, and timely delivery, completing the supply chain loop.
6. Customers/Consumers
Customers are the final point in the chain. Their demand drives production, distribution, and inventory decisions, making them a critical component of any supply chain network.
You May Also Like to Read: Challenges in Supply Chain Operations
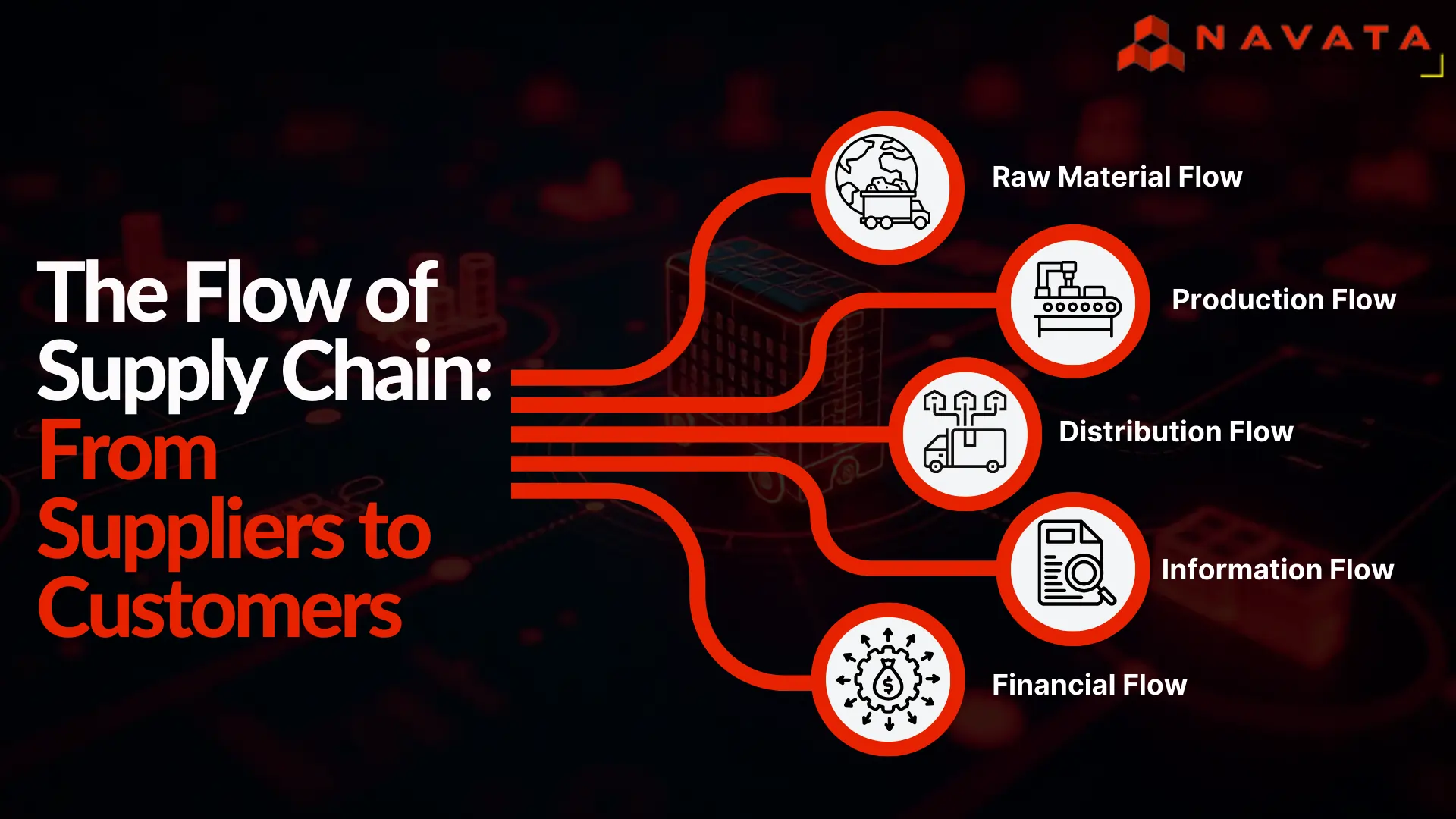
How Supply Chain Work?
A supply chain functions as a continuous, interconnected system where every stage affects the next. Understanding each flow gives insight into how goods, information, and finances move efficiently from origin to customer.
1. Raw Material Flow
Raw materials move from suppliers to manufacturers. This stage includes sourcing, quality checks, and transportation. Delays, poor quality, or shortages here can halt production and disrupt the entire chain.
2. Production Flow
Manufacturers transform raw materials into finished goods. Efficient production requires proper scheduling, quality control, and resource allocation. Bottlenecks in production can increase costs, extend lead times, and affect customer satisfaction.
3. Distribution Flow
Distribution covers moving finished goods from factories to warehouses, retailers, or directly to consumers. It includes logistics planning, transport management, and storage. Any inefficiency can delay deliveries, increase operational costs, and reduce competitiveness.
4. Information Flow
Information flow involves real-time communication about orders, inventory levels, demand forecasts, and shipments. Accurate and timely data ensures coordination across suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, preventing errors and improving responsiveness.
5. Financial Flow
Financial flow manages payments, credits, and settlements across all participants. Smooth financial transactions maintain supplier relationships, ensure timely production, and support uninterrupted operations. Delays or errors can disrupt the entire supply chain ecosystem.
Each flow is interdependent. A disruption in any stage—whether raw material shortages, production delays, mismanaged distribution, inaccurate information, or financial issues—can ripple through the entire network, affecting efficiency, costs, and customer satisfaction.
Also, Read our Blog on AI-Driven Predictive Supply Chains
Why Understanding Supply Chain is Important?
Understanding the supply chain gives insight into how products reach you efficiently. It helps you:
- Recognize the journey of products from origin to consumer.
- Identify potential points of delay or inefficiency.
- Understand how disruptions impact availability, costs, and service quality.
Real-World Examples:
A smartphone’s supply chain involves sourcing metals, assembling components in factories, transporting to warehouses, and delivering to stores or customers.
Grocery products move from farms to processing centers, distribution hubs, and supermarkets before reaching households.
Optimize Your Supply Chain with Experts!
Smarter solutions for seamless supply chains.
Key Takeaways
A supply chain is the network, not the management of it.
It includes people, processes, and resources that move goods from origin to customer.
Every stage is interdependent; disruptions affect the full network.
Understanding the chain helps anticipate delays, optimize flows, and improve reliability.
A supply chain is more than a sequence of steps—it’s a connected network where every participant and process matters. Understanding it gives insight into how products reach you efficiently, safely, and reliably.
Thanks For Reading: What is Supply Chain and How It Works?
Powered By 360Presence
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a supply chain in simple terms?
It is the network moving products from suppliers to customers while managing information, finances, and operational efficiency.
Q2. Why is the supply chain important in business?
It impacts cost, delivery speed, risk management, and customer satisfaction.
Q3. What makes a supply chain effective?
Reliable suppliers, flexible production, accurate inventory management, optimized logistics, and predictive technology.
Q4. How is AI changing supply chains?
AI in supply chain improves forecasting, logistics optimization, risk prediction, and operational efficiency, enabling proactive decision-making.
Q5. What is the future of supply chains?
Predictive, automated, sustainable, and transparent systems will dominate, improving speed, reliability, and scalability.