Road Transportation Vs Water Transportation
Transportation is the backbone of logistics, ensuring goods move efficiently from one point to another. Businesses must choose the right mode to balance cost, speed, and environmental impact. This Blog on Road transportation vs water transportation will help in key comparison when planning logistics strategies. Road transport offers flexibility and faster delivery for short to medium distances, making it ideal for perishable and time-sensitive goods.
On the other hand, water transport is cost-effective for moving large volumes over long distances, especially in international trade. Each mode has its advantages and limitations, depending on cargo type, destination, and budget, helping businesses make informed decisions to optimize their supply chain operations.
Overview of Road Transportation
Road transportation refers to the movement of goods and passengers using vehicles on roads and highways. It plays a crucial role in logistics due to its accessibility, flexibility, and ability to provide direct deliveries without reliance on ports or terminals. This model is widely used for short to medium-distance shipments and offers faster transit times compared to other transportation methods.
Common Vehicles Used in Road Transport
Trucks – Used for long-haul freight, with variations like container trucks, refrigerated trucks, and tankers for different cargo types.
Vans – Ideal for small shipments, courier services, and last-mile deliveries.
Buses and Commercial Vehicles – Used for passenger transport and light goods movement.
Key Industries Relying on Road Transport
E-commerce & Retail – Ensures quick and efficient last-mile delivery.
FMCG & Food Industry – Supports transportation of perishable and packaged goods.
Manufacturing & Construction – Moves raw materials, machinery, and finished products to distribution centers or sites.
Pharmaceuticals – Ensures timely delivery of medicines and medical supplies.
Road transportation remains a preferred choice due to its speed, convenience, and ability to handle various cargo types across diverse locations.
Overview of Water Transportation
Water transportation involves the movement of goods and passengers across rivers, lakes, and oceans using ships, barges, and ferries. It is a vital component of global trade, handling over 80% of international freight. This mode is particularly beneficial for transporting large volumes of goods over long distances at a lower cost compared to road or air transport. Though slower, it is highly efficient for bulk shipments and plays a crucial role in international supply chains.
Types of Vessels Used in Water Transport
Cargo Ships – Used for containerized freight, dry bulk (coal, grains), and liquid bulk (oil, chemicals).
Barges – Flat-bottomed vessels ideal for inland waterways and heavy cargo.
Ferries – Transport passengers and vehicles across short water routes.
Key Industries Dependent on Water Transport
Shipping & Logistics – Facilitates international trade by moving raw materials and finished goods.
Oil & Gas – Transports crude oil, LNG, and petroleum products.
Mining & Agriculture – Moves bulk commodities like coal, iron ore, and grains.
Automotive Industry – Ships vehicles globally through roll-on/roll-off (RoRo) vessels.
Water transport remains essential for cost-effective and large-scale global logistics, supporting industries that require efficient bulk movement across continents.
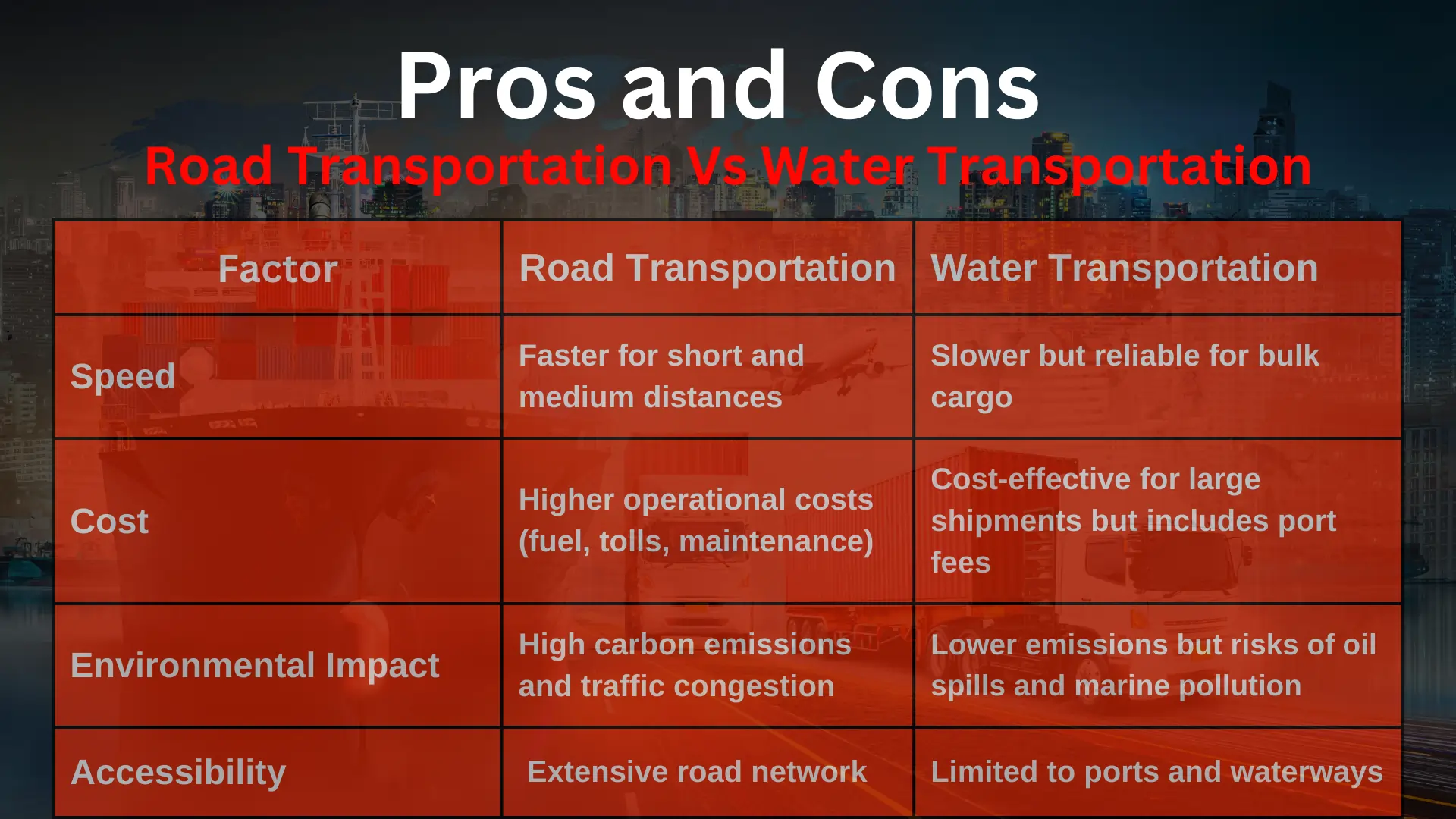
Pros & Cons of Road Transportation and Water Transportation
Pros and Cons of Road Transportation
Pros
Faster for Short Distances
Road transport is the best choice for regional and domestic deliveries, ensuring quick and efficient movement of goods. Unlike water transport, which involves port handling, road transport allows direct and faster transit times.
Door-to-Door Delivery
Unlike water transport, which requires additional handling at ports, road transport provides seamless door-to-door service, reducing delays, transit costs, and handling risks.
Extensive Accessibility and Flexibility
Road transport can reach urban, rural, and remote areas without reliance on waterways or terminals. This flexibility makes it ideal for industries requiring last-mile connectivity.
Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring
Equipped with GPS and fleet management systems, road transport allows real-time shipment tracking, optimizing routes, reducing risks, and improving logistics efficiency.
Cons
High Fuel and Maintenance Costs
Road transport involves high fuel costs, toll charges, frequent vehicle maintenance, and rising fuel price fluctuations, making it an expensive option for long-distance freight.
Traffic Congestion and Delays
Road conditions, accidents, and urban congestion can lead to unpredictable delays, affecting delivery timelines and overall supply chain efficiency.
Not Suitable for Bulk Shipments
Trucks and vans have limited capacity, making them less efficient for transporting heavy or oversized cargo compared to ships, which handle bulk freight more cost-effectively.
Pros and Cons of Water Transportation
Pros
Cost-effective for Large Volumes
Ships can transport massive cargo loads at a significantly lower cost per ton compared to road transport. This makes water transport ideal for industries handling bulk commodities like coal, oil, minerals, and agricultural products.
Lower Fuel Consumption per Ton
Water transport is far more fuel-efficient than road transport for long-distance shipments. Ships consume less fuel per ton of cargo, leading to lower transportation costs and reduced environmental impact.
Ideal for Long-Distance and International Trade
Water transport is the backbone of global trade, moving goods efficiently across continents. It is best suited for international freight, allowing businesses to transport large volumes over vast distances with cost efficiency.
Cons
Slow Transit Times
Ships take significantly longer to transport goods compared to road transport. Factors like long distances, port clearance procedures, and weather-related delays can further extend shipping times, making it unsuitable for urgent deliveries.
Limited to Coastal and Inland Ports
Water transportation is restricted to areas with port and waterway access. Inland destinations require multimodal transport, often involving road or rail, adding complexity to logistics.
Additional Handling Costs at Ports
Despite lower per-ton shipping costs, businesses must account for port handling fees, customs duties, and container loading/unloading expenses, increasing overall logistics costs.
Conclusion
Both road and water transportation play vital roles in logistics, each offering unique advantages based on cargo type, cost, and delivery timelines. Road transport is ideal for short to medium distances, ensuring faster and more flexible deliveries, while water transport excels in moving bulk goods cost-effectively over long distances. Businesses must assess their logistical needs, considering factors like speed, infrastructure, and environmental impact. A strategic combination of both modes can enhance supply chain efficiency and optimize transportation costs.
Thank You For Reading: Road Transportation Vs Water Transportation
Powered By 360Presence

