Cargo Theft in Logistics
Cargo theft in logistics is an escalating concern, with incidents hitting record levels in 2024, marking a 14% increase from 2023. Criminals are drawn to shipments for their high resale value and are employing increasingly advanced tactics, including identity theft, document forgery, and phishing scams, to infiltrate supply chains.
The impact of cargo theft in logistics extends beyond financial losses, disrupting supply chains, delaying deliveries, and damaging brand reputation. As theft methods evolve, businesses must stay ahead by implementing robust security measures to safeguard their shipments. From hijackings to cyber-enabled fraud, logistics companies face ever-changing risks that require a combination of physical security, technology, and employee awareness to mitigate.
Preventing cargo theft is no longer optional—it is essential for maintaining operational efficiency, ensuring customer trust, and protecting valuable assets. By adopting proactive security strategies, businesses can minimize risks and strengthen the resilience of their supply chains.

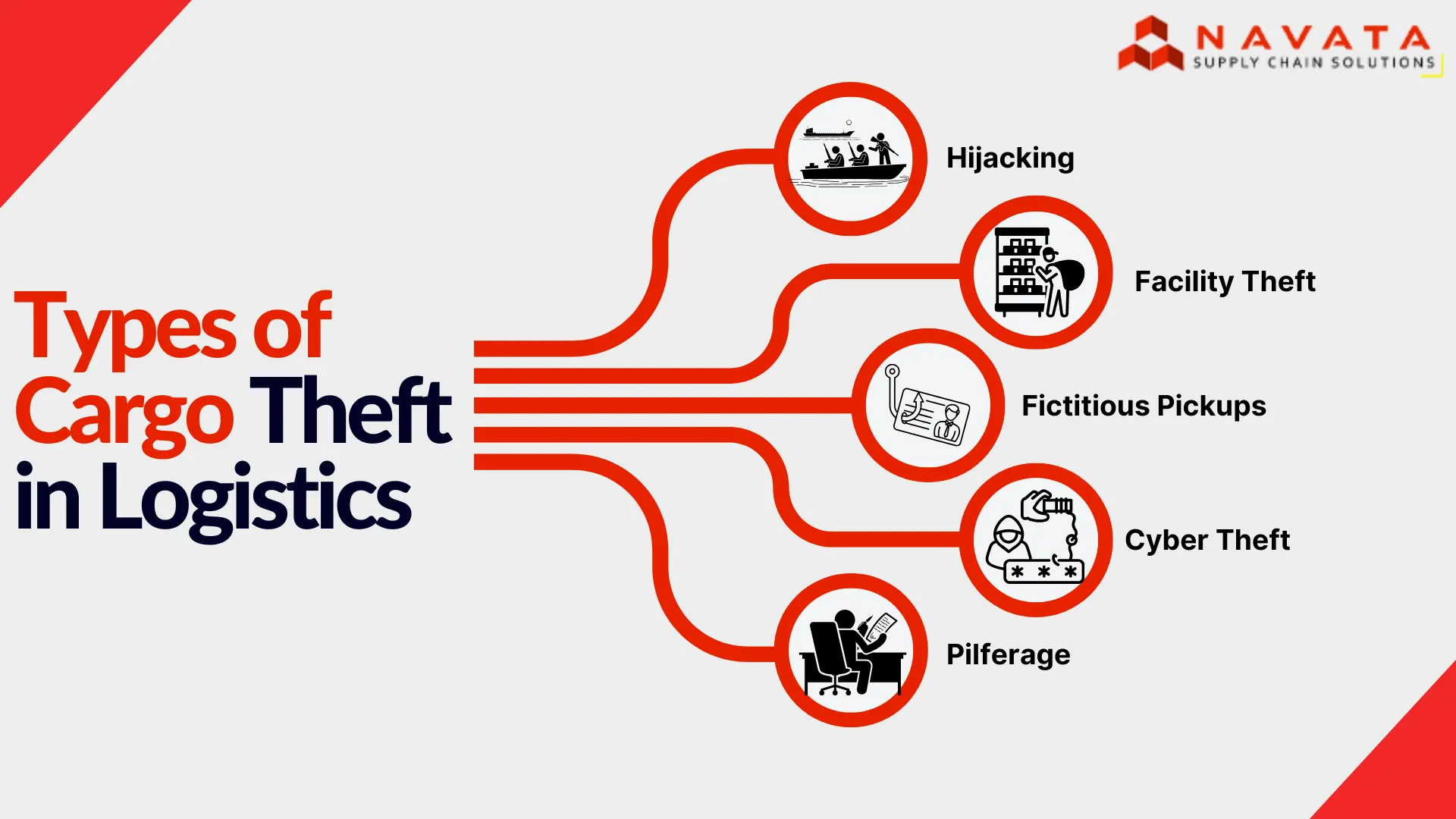
Types of Cargo Theft in Logistics
Hijacking
During transportation criminals hijack cargo through the use of force or deception or weapons and threats. Criminals target transport vehicles during both rest stops and active travel which leads to major financial losses and endangerment of drivers’ security.
Facility Theft
Theft incidents at facilities frequently occur because warehouses and distribution centers and loading docks remain unprotected. Theft of valuable goods requires strong surveillance and secure entry points and no assistance from insiders so businesses must focus on robust access control and monitoring to stop these incidents.
Fictitious Pickups
Criminal operators pretend to be authorized transport companies through the use of bogus documents or stolen identification documents to obtain delivery consignments. Theft through such methods proves challenging to detect because criminals use verification procedure gaps to their advantage which requires both strict identity verification and digital tracking systems to prevent it.
Cyber Theft
Theft through hacking involves the manipulation of logistics systems followed by data theft about shipments leading to fraudulent cargo rerouting. The ability of criminals to steal digital supply chain information depends on phishing scams and ransomware attacks and system breaches thus making cybersecurity vital for protection.
Pilferage
Theft through pilferage happens when staff members and inside personnel steal goods little by little over extended periods of time. The absence of inventory discrepancies often remains undetected until discrepancies become apparent, so regular audits and employee background checks with strict monitoring become essential to stop continuing losses.
You May Also Like to Read: What is IoT and how it is Shaping Supply Chain & Logistics
Factors Contributing to Cargo Theft in Logistics
Inadequate Security
Poor warehouse and transit point security creates an environment where cargo remains exposed to theft. Criminals take advantage of inadequate security measures when warehouses lack proper surveillance, weak access control and minimal security personnel create easy points for theft.
Poor Tracking and Monitoring Systems
Real-time tracking systems play a crucial role in recovering stolen shipments because their absence makes the recovery process difficult. Businesses remain uninformed about transportation route changes, unauthorized stops and hijacking dangers because they lack GPS monitoring, RFID tags, and geofencing alert systems.
Lack of Driver Awareness
The lack of driver training and awareness makes them vulnerable to theft through deception methods and hijacking attempts. The risk of cargo loss increases because drivers need proper training about security protocols rest stop safety and emergency response procedures.
Weak Cyber Defenses
The vulnerability of IT security systems creates an opening for cybercriminals who breach data, reroute cargo, and conduct fraudulent activities. Logistics networks remain exposed to phishing attacks and digital fraud together with ransomware because they lack essential security measures including firewalls and encryption technologies as well as multi-factor authentication systems.
Strategies to Prevent Cargo Theft in Logistics
Strengthening Physical Security
Physical security must be established with strength to stop cargo theft incidents. Secured parking coupled with designated rest stops serves as an effective security measure against hijacking since thieves prefer to target vehicles that remain unattended. Security systems with surveillance cameras together with alarm systems should be installed throughout warehouses to prevent unauthorized entry. Both tamper-proof locking systems and truck GPS monitors provide enhanced cargo protection by enabling real-time position tracking. Multiple layers of security that these measures provide make shipments more difficult to intercept or steal by criminals.
Technology-Based Solutions
The prevention of cargo theft heavily depends on advanced technological solutions. The use of GPS tracking in combination with RFID systems allows logistics providers to monitor their supply chain products in real time. This approach provides full supply chain visibility. Geofencing alerts generated by the system immediately notify logistics professionals about unauthorized route detours which helps stop cargo hijacking and diverting incidents. Through predictive analytics that uses artificial intelligence system, logistic operators can discover vulnerable areas and develop alternative secure routes. Businesses who integrate these technologies will be able to actively reduce risks which results in enhanced security and efficiency during cargo delivery and storage processes.
Employee Training and Awareness
Organizations must provide essential education for both their drivers and warehouse personnel because this approach helps minimize cargo theft occurrences. The training programs must teach employees to detect suspicious activities while teaching them proper cargo security measures and safety procedures. All drivers must learn proper emergency procedures that they need to execute when hijacking attempts occur. The establishment of secure reporting channels helps workers develop better internal security awareness. A workforce trained to high standards functions as an initial defense mechanism for detecting and responding to potential theft occurrences in a timely manner.
Strengthening Cybersecurity Measures
Digital infrastructure protection in logistics security matches the importance of protecting physical cargo because cyber threats against logistics operations are increasing rapidly. The implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) for database access stops unauthorized breaches from occurring. System protection against hacking attempts becomes successful through periodic software updates combined with cybersecurity audit inspections. Employees need training to identify both phishing attacks and social engineering attempts that aim to extract sensitive information from staff members. Companies that strengthen cybersecurity defenses stop digital attacks that protect their shipment data from cybercriminals.
Collaboration and Regulatory Compliance
Cooperation with law enforcement departments together with industry groups and regulatory organizations creates stronger protection against cargo theft. Strategic partnerships enable quick reaction to theft occurrences and promote better information exchange regarding developing security threats. Businesses can maintain their security leadership by implementing best practices that government agencies recommend. Regular audits help businesses maintain safety compliance which decreases the vulnerabilities that exist within their supply chain operations. A strengthened logistics network through collaborative work becomes harder for criminals to penetrate because of its increased resistance to system vulnerabilities.

Conclusion
Cargo theft in logistics is still a major concern, necessitating aggressive security measures to secure supply networks. As thieves deploy increasingly sophisticated strategies, firms must improve physical security, use technology, train staff, and boost cybersecurity to limit threats. Real-time tracking, strong identification verification, and engagement with law enforcement are critical for combating theft.
Companies can protect assets, preserve operational efficiency, and maintain consumer trust by addressing security at all stages, from warehouses to transit routes. Implementing comprehensive theft prevention techniques not only reduces financial losses but also improves the robustness and dependability of the global logistics network.
Thanks For Reading: What is Cargo Theft in Logistics & How to Prevent Them?
Powered By 360Presence

